Lost in Trans-IL-6 Signaling: Alveolar Type II Cell Death in Emphysema
- PMID: 27976936
- PMCID: PMC5215037
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201607-1441ED
Lost in Trans-IL-6 Signaling: Alveolar Type II Cell Death in Emphysema
Figures
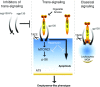
Comment on
-
Therapeutic Targeting of the IL-6 Trans-Signaling/Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Complex 1 Axis in Pulmonary Emphysema.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016 Dec 15;194(12):1494-1505. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201512-2368OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016. PMID: 27373892
References
-
- Ruwanpura SM, McLeod L, Dousha LF, Seow HJ, Alhayyani S, Tate MD, Deswaerte V, Brooks GD, Bozinovski S, MacDonald M, et al. Therapeutic targeting of the IL-6 trans-signaling/mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 axis in pulmonary emphysema. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;194:1494–1505. - PubMed
-
- Ruwanpura SM, McLeod L, Brooks GD, Bozinovski S, Vlahos R, Longano A, Bardin PG, Anderson GP, Jenkins BJ. IL-6/Stat3-driven pulmonary inflammation, but not emphysema, is dependent on interleukin-17A in mice. Respirology. 2014;19:419–427. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

