Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase in Asthma: Novel Roles and Therapeutic Approaches
- PMID: 27977296
- PMCID: PMC5516292
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0308TR
Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase in Asthma: Novel Roles and Therapeutic Approaches
Abstract
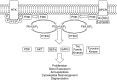
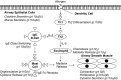
Asthma manifests as airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation, including coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Immune cells and airway structural cells orchestrate asthma pathophysiology, leading to mucus secretion, airway narrowing, and obstruction. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase, a lipid kinase, plays a crucial role in many of the cellular and molecular mechanisms driving asthma pathophysiology and represents an attractive therapeutic target. Here, we summarize the diverse roles of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in the pathogenesis of asthma and discuss novel therapeutic approaches to treatment.
Keywords: asthma; bronchodilator; inflammation; phosphoinositide 3-kinase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinase δ for allergic asthma.Biochem Soc Trans. 2012 Feb;40(1):240-5. doi: 10.1042/BST20110665. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012. PMID: 22260698 Review.
-
PI 3-kinase inhibition: a therapeutic target for respiratory disease.Biochem Soc Trans. 2004 Apr;32(Pt 2):378-82. doi: 10.1042/bst0320378. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. PMID: 15046612 Review.
-
Inhibition of phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta attenuates allergic airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in murine asthma model.FASEB J. 2006 Mar;20(3):455-65. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-5045com. FASEB J. 2006. PMID: 16507763
-
An anti-inflammatory role for a phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor LY294002 in a mouse asthma model.Int Immunopharmacol. 2005 Mar;5(3):495-502. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2004.10.015. Int Immunopharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15683846
-
The pathophysiological roles of PI3Ks and therapeutic potential of selective inhibitors in allergic inflammation.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2010;152 Suppl 1:90-5. doi: 10.1159/000312132. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20523070 Review.
Cited by
-
PI3Kγδ inhibition suppresses key disease features in a rat model of asthma.Respir Res. 2024 Apr 23;25(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02814-1. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 38654248 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical characterization of CPL302-253, a selective inhibitor of PI3Kδ, as the candidate for the inhalatory treatment and prevention of Asthma.PLoS One. 2020 Jul 23;15(7):e0236159. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236159. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32702053 Free PMC article.
-
A practical guideline of genomics-driven drug discovery in the era of global biobank meta-analysis.Cell Genom. 2022 Oct 12;2(10):100190. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2022.100190. eCollection 2022 Oct 12. Cell Genom. 2022. PMID: 36778001 Free PMC article.
-
A high-throughput 3D cantilever array to model airway smooth muscle hypercontractility in asthma.APL Bioeng. 2023 May 16;7(2):026104. doi: 10.1063/5.0132516. eCollection 2023 Jun. APL Bioeng. 2023. PMID: 37206658 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic changes during TGF-β-mediated differentiation of airway fibroblasts to myofibroblasts.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 30;9(1):20377. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56955-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31889146 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

