Peptide Processing Is Critical for T-Cell Memory Inflation and May Be Optimized to Improve Immune Protection by CMV-Based Vaccine Vectors
- PMID: 27977791
- PMCID: PMC5158087
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006072
Peptide Processing Is Critical for T-Cell Memory Inflation and May Be Optimized to Improve Immune Protection by CMV-Based Vaccine Vectors
Abstract
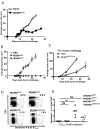
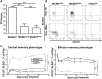
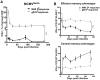
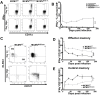
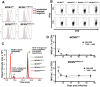
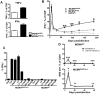
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) elicits long-term T-cell immunity of unparalleled strength, which has allowed the development of highly protective CMV-based vaccine vectors. Counterintuitively, experimental vaccines encoding a single MHC-I restricted epitope offered better immune protection than those expressing entire proteins, including the same epitope. To clarify this conundrum, we generated recombinant murine CMVs (MCMVs) encoding well-characterized MHC-I epitopes at different positions within viral genes and observed strong immune responses and protection against viruses and tumor growth when the epitopes were expressed at the protein C-terminus. We used the M45-encoded conventional epitope HGIRNASFI to dissect this phenomenon at the molecular level. A recombinant MCMV expressing HGIRNASFI on the C-terminus of M45, in contrast to wild-type MCMV, enabled peptide processing by the constitutive proteasome, direct antigen presentation, and an inflation of antigen-specific effector memory cells. Consequently, our results indicate that constitutive proteasome processing of antigenic epitopes in latently infected cells is required for robust inflationary responses. This insight allows utilizing the epitope positioning in the design of CMV-based vectors as a novel strategy for enhancing their efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest: Oregon Health and Science University (OHSU) and KF have a significant financial interest in TomegaVax Inc., a company that may have a commercial interest in the results of this research and technology. LCS was a paid consultant of Tomegavax in 2015. This potential individual and institutional conflict of interest has been reviewed and managed by OHSU. RBR and CM have been employed by TomegaVax, Inc., a commercial company. The authors declare that there are no further financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Klenerman P, Oxenius A. T cell responses to cytomegalovirus. Nature reviews Immunology. 2016. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

