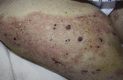
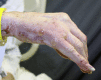
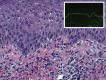
Development of bullous pemphigoid during nivolumab therapy
- PMID: 27981213
- PMCID: PMC5144742
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2016.05.009
Development of bullous pemphigoid during nivolumab therapy
Keywords: BP, bullous pemphigoid; Bregs, B regulatory cells; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte–associated protein 4; IRAE, immune-related adverse events; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1, programmed death ligand 1; bullous pemphigoid; nivolumab; pembrolizumab; programmed cell death protein 1; programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitor.
Figures
References
-
- Hwang S.J., Carlos G., Wakade D. Cutaneous adverse events (AEs) of anti-programmed cell death (PD)-1 therapy in patients with metastatic melanoma: A single-institution cohort. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:455–461.e1. - PubMed
-
- Hwang S.J., Carlos G., Chou S., Wakade D., Carlino M.S., Fernandez-Penas P. Bullous pemphigoid, an autoantibody-mediated disease, is a novel immune-related adverse event in patients treated with anti-programmed cell death 1 antibodies. Melanoma Res. 2016;26:413–416. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials