Non-Viral CRISPR/Cas Gene Editing In Vitro and In Vivo Enabled by Synthetic Nanoparticle Co-Delivery of Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA
- PMID: 27981708
- PMCID: PMC5521011
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201610209
Non-Viral CRISPR/Cas Gene Editing In Vitro and In Vivo Enabled by Synthetic Nanoparticle Co-Delivery of Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA
Abstract
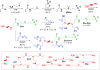
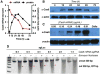
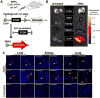
CRISPR/Cas is a revolutionary gene editing technology with wide-ranging utility. The safe, non-viral delivery of CRISPR/Cas components would greatly improve future therapeutic utility. We report the synthesis and development of zwitterionic amino lipids (ZALs) that are uniquely able to (co)deliver long RNAs including Cas9 mRNA and sgRNAs. ZAL nanoparticle (ZNP) delivery of low sgRNA doses (15 nm) reduces protein expression by >90 % in cells. In contrast to transient therapies (such as RNAi), we show that ZNP delivery of sgRNA enables permanent DNA editing with an indefinitely sustained 95 % decrease in protein expression. ZNP delivery of mRNA results in high protein expression at low doses in vitro (<600 pM) and in vivo (1 mg kg-1 ). Intravenous co-delivery of Cas9 mRNA and sgLoxP induced expression of floxed tdTomato in the liver, kidneys, and lungs of engineered mice. ZNPs provide a chemical guide for rational design of long RNA carriers, and represent a promising step towards improving the safety and utility of gene editing.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas; gene editing; mRNA delivery; nanoparticles; sgRNA delivery.
© 2017 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures


References
-
- Jinek M, Chylinski K, Fonfara I, et al. Science. 2012;337:816–821. - PMC - PubMed
- Cong L, Ran FA, Cox D, et al. Science. 2013;339:819–823. - PMC - PubMed
- Mali P, Yang LH, Esvelt KM, et al. Science. 2013;339:823–826. - PMC - PubMed
- Sanchez-Rivera FJ, Jacks T. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15:387–395. - PMC - PubMed
- Sander JD, Joung JK. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32:347–355. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Platt RJ, Chen SD, Zhou Y, et al. Cell. 2014;159:440–455. - PMC - PubMed
- Sanchez-Rivera FJ, Papagiannakopoulos T, Romero R, et al. Nature. 2014;516:428–431. - PMC - PubMed
- Xue W, Chen S, Yin H, et al. Nature. 2014;514:380–384. - PMC - PubMed
- Yin H, Xue W, Chen S, et al. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32:551–553. - PMC - PubMed
- Chen SD, Sanjana NE, Zheng KJ, et al. Cell. 2015;160:1246–1260. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

