Half-Sandwich Ru(II) Halogenido, Valproato and 4-Phenylbutyrato Complexes Containing 2,2'-Dipyridylamine: Synthesis, Characterization, Solution Chemistry and In Vitro Cytotoxicity
- PMID: 27983703
- PMCID: PMC6274116
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21121725
Half-Sandwich Ru(II) Halogenido, Valproato and 4-Phenylbutyrato Complexes Containing 2,2'-Dipyridylamine: Synthesis, Characterization, Solution Chemistry and In Vitro Cytotoxicity
Abstract
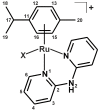
Halogenido and carboxylato Ru(II) half-sandwich complexes of the general composition [Ru(η⁶-p-cym)(dpa)X]PF₆ (1-5) were prepared and thoroughly characterized with various techniques (e.g., mass spectrometry, NMR spectroscopy and X-ray analysis); dpa = 2,2'-dipyridylamine; p-cym = p-cymene; X = Cl- (for 1), Br- (for 2), I- (for 3), valproate(1-) (for 4) or 4-phenylbutyrate(1-) (for 5). A single-crystal X-ray analysis showed a pseudo-octahedral piano-stool geometry of [Ru(η⁶-p-cym)(dpa)I]PF₆ (3), with a η⁶-coordinated p-cymene, bidentate N-donor dpa ligand and iodido ligand coordinated to the Ru(II) atom. The results of the ¹H-NMR solution behaviour studies proved that the complexes 1-5 hydrolyse were in the mixture of solvents used (10% MeOD-d₄/90% D₂O). Complexes 1-5 were in vitro inactive against the A2780 human ovarian carcinoma cell line, up to the highest tested concentration (IC50 > 100 μM).
Keywords: 2,2′-dipyridylamine; X-ray structure; half-sandwich; in vitro cytotoxicity; ruthenium; solution behaviour.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures











References
-
- Murray B.S., Babak M.V., Hartinger C.G., Dyson P.J. The development of RAPTA compounds for the treatment of tumors. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016;306:86–114. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2015.06.014. - DOI
-
- Romero-Canelón I., Salassa L., Sadler P.J. The contrasting activity of iodido versus chlorido ruthenium and osmium arene azo- and imino-pyridine anticancer complexes: Control of cell selectivity, cross-resistance, p53 dependence, and apoptosis pathway. J. Med. Chem. 2013;56:1291–1300. doi: 10.1021/jm3017442. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

