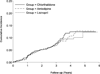
Treatment-Resistant Hypertension and Outcomes Based on Randomized Treatment Group in ALLHAT
- PMID: 27984005
- PMCID: PMC5362319
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.10.002
Treatment-Resistant Hypertension and Outcomes Based on Randomized Treatment Group in ALLHAT
Abstract
Background: Although hypertension guidelines define treatment-resistant hypertension as blood pressure uncontrolled by ≥3 antihypertensive medications, including a diuretic, it is unknown whether patient prognosis differs when a diuretic is included.
Methods: Participants in the Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT) were randomly assigned to first-step therapy with chlorthalidone, amlodipine, or lisinopril. At a Year 2 follow-up visit, those with average blood pressure ≥140 mm Hg systolic or ≥90 mm Hg diastolic on ≥3 antihypertensive medications, or blood pressure <140/90 mm Hg on ≥4 antihypertensive medications were identified as having apparent treatment-resistant hypertension. The prevalence of treatment-resistant hypertension and its association with ALLHAT primary (combined fatal coronary heart disease or nonfatal myocardial infarction) and secondary (all-cause mortality, stroke, heart failure, combined coronary heart disease, and combined cardiovascular disease) outcomes were identified for each treatment group.
Results: Of participants assigned to chlorthalidone, amlodipine, or lisinopril, 9.6%, 11.4%, and 19.7%, respectively, had treatment-resistant hypertension. During mean follow-up of 2.9 years, primary outcome incidence was similar for those assigned to chlorthalidone compared with amlodipine or lisinopril (amlodipine- vs chlorthalidone-adjusted hazard ratio [HR] 0.86; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.53-1.39; P = .53; lisinopril- vs chlorthalidone-adjusted HR = 1.06; 95% CI, 0.70-1.60; P = .78). Secondary outcome risks were similar for most comparisons except coronary revascularization, which was higher with amlodipine than with chlorthalidone (HR 1.86; 95% CI, 1.11-3.11; P = .02). An as-treated analysis based on diuretic use produced similar results.
Conclusions: In this study, which titrated medications to a goal, participants assigned to chlorthalidone were less likely to develop treatment-resistant hypertension. However, prognoses in those with treatment-resistant hypertension were similar across treatment groups.
Keywords: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; Calcium channel blocker; Diuretics; Hypertension; Resistance.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The other authors report no conflicts.
Figures
References
-
- Calhoun DA, Jones D, Textor S, et al. Resistant hypertension: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Circulation. 2008;117(25):e510–e526. - PubMed
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association. 2003;289(19):2560–2571. - PubMed
-
- Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, et al. 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur Heart J. 2013;34(28):2159–2219. - PubMed
-
- National Clinical Guideline Centre. The clinical management of primary hypertension in adults. http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/index.jsp?action=download&o=53228. London: National Clinical Guideline Centre; 2011. [Accessed Dec 03, 2011]. [cited 2011 December 03]; Available from: http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/index.jsp?action=download&o=53228.
-
- Muntner P, Davis BR, Cushman WC, et al. Treatment-resistant hypertension and the incidence of cardiovascular disease and end-stage renal disease: results from the Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT) Hypertension. 2014;64(5):1012–1021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical