The C. elegans Discoidin Domain Receptor DDR-2 Modulates the Met-like RTK-JNK Signaling Pathway in Axon Regeneration
- PMID: 27984580
- PMCID: PMC5161311
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006475
The C. elegans Discoidin Domain Receptor DDR-2 Modulates the Met-like RTK-JNK Signaling Pathway in Axon Regeneration
Abstract
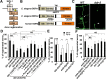
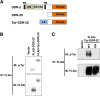
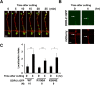
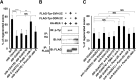
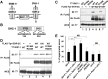
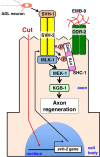
The ability of specific neurons to regenerate their axons after injury is governed by cell-intrinsic regeneration pathways. However, the signaling pathways that orchestrate axon regeneration are not well understood. In Caenorhabditis elegans, initiation of axon regeneration is positively regulated by SVH-2 Met-like growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signaling through the JNK MAPK pathway. Here we show that SVH-4/DDR-2, an RTK containing a discoidin domain that is activated by collagen, and EMB-9 collagen type IV regulate the regeneration of neurons following axon injury. The scaffold protein SHC-1 interacts with both DDR-2 and SVH-2. Furthermore, we demonstrate that overexpression of svh-2 and shc-1 suppresses the delay in axon regeneration observed in ddr-2 mutants, suggesting that DDR-2 functions upstream of SVH-2 and SHC-1. These results suggest that DDR-2 modulates the SVH-2-JNK pathway via SHC-1. We thus identify two different RTK signaling networks that play coordinated roles in the regulation of axonal regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- O’Brien GS, Sagasti A (2009) Fragile axons forge the path to gene discovery: a MAP kinase pathway regulates axon regeneration. Sci Signal 2: e30. - PubMed
-
- Camps M, Nichols A, Arkinstall S (2000) Dual specificity phosphatases: a gene family for control of MAP kinase function. FASEB J 14: 6–16. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

