Impact of age and comorbidity on treatment of non-small cell lung cancer recurrence following complete resection: A nationally representative cohort study
- PMID: 27987578
- PMCID: PMC5172386
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.11.002
Impact of age and comorbidity on treatment of non-small cell lung cancer recurrence following complete resection: A nationally representative cohort study
Abstract
Objective: Older patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) are less likely to receive guideline-recommended treatment at diagnosis, independent of comorbidity. However, national data on treatment of postoperative recurrence are limited. We evaluated the associations between age, comorbidity, and other patient factors and treatment of postoperative NSCLC recurrence in a national cohort.
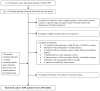
Materials and methods: We randomly selected 9001 patients with surgically resected stage I-III NSCLC in 2006-2007 from the National Cancer Data Base. Patients were followed for 5 years or until first NSCLC recurrence, new primary cancer, or death, whichever came first. Perioperative comorbidities, first recurrence, treatment of recurrence, and survival were abstracted from medical records and merged with existing registry data. Factors associated with active treatment (chemotherapy, radiation, and/or surgery) versus supportive care only were analyzed using multivariable logistic regression.
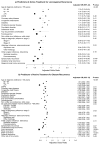
Results: Median age at initial diagnosis was 67; 69.7% had >1 comorbidity. At 5-year follow-up, 12.3% developed locoregional and 21.5% developed distant recurrence. Among patients with locoregional recurrence, 79.5% received active treatment. Older patients (OR 0.49 for age >75 compared with <55; 95% CI 0.27-0.88) and those with substance abuse (OR 0.43; 95% CI 0.23-0.81) were less likely to receive active treatment. Women (OR 0.62; 95% CI 0.43-0.89) and patients with symptomatic recurrence (OR 0.69; 95% CI 0.47-0.99) were also less likely to receive active treatment. Among those with distant recurrence, 77.3% received active treatment. Older patients (OR 0.42 for age >75 compared with <55; 95% CI 0.26-0.68) and those with any documented comorbidities (OR 0.59; 95% CI 0.38-0.89) were less likely to receive active treatment.
Conclusion: Older patients independent of comorbidity, patients with substance abuse, and women were less likely to receive active treatment for postoperative NSCLC recurrence. Studies to further characterize these disparities in treatment of NSCLC recurrence are needed to identify barriers to treatment.
Keywords: Geriatric oncology; Non-small cell lung cancer; Recurrence; Treatment.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Timothy L. McMurry has received consulting support from Diffusion Pharmaceuticals. Amanda B. Francescatti has stock ownership in ICAD. George J. Chang has received consulting support from Ethicon. Caprice C. Greenberg has received grant funding from Covidien-Medtronic and consulting support from Johnson and Johnson. The remaining authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Miller D, Bishop K, Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, Mariotto A, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, CKA . SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2013. National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD: [accessed May 1, 2016]. http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2013/
-
- Colt HG, Murgu SD, Korst RJ, Slatore CG, Unger M, Quadrelli S. Follow-up and surveillance of the patient with lung cancer after curative-intent therapy: Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013;143(5 Suppl):e437S–54S. - PubMed
-
- Sugimura H, Nichols FC, Yang P, Allen MS, Cassivi SD, Deschamps C, Williams BA, Pairolero PC. Survival after recurrent nonsmall-cell lung cancer after complete pulmonary resection. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;83(2):409–18. - PubMed
-
- Taylor MD, Nagji AS, Bhamidipati CM, Theodosakis N, Kozower BD, Lau CL, Jones DR. Tumor recurrence after complete resection for non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2012;93(6):1813–21. - PubMed
-
- Ujiie H, Kadota K, Chaft JE, Buitrago D, Sima CS, Lee MC, Huang J, Travis WD, Rizk NP, Rudin CM, Jones DR, Adusumilli PS. Solid Predominant Histologic Subtype in Resected Stage I Lung Adenocarcinoma Is an Independent Predictor of Early, Extrathoracic, Multisite Recurrence and of Poor Postrecurrence Survival. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(26):2877–84. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

