Virus-Enabled Biosensor for Human Serum Albumin
- PMID: 27989106
- PMCID: PMC5518940
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04840
Virus-Enabled Biosensor for Human Serum Albumin
Abstract
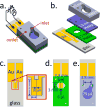
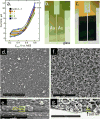
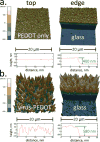
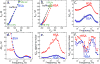
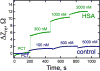
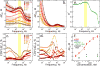
The label-free detection of human serum albumin (HSA) in aqueous buffer is demonstrated using a simple, monolithic, two-electrode electrochemical biosensor. In this device, both millimeter-scale electrodes are coated with a thin layer of a composite containing M13 virus particles and the electronically conductive polymer poly(3,4-ethylenedioxy thiophene) or PEDOT. These virus particles, engineered to selectively bind HSA, serve as receptors in this biosensor. The resistance component of the electrical impedance, Zre, measured between these two electrodes provides electrical transduction of HSA binding to the virus-PEDOT film. The analysis of sample volumes as small as 50 μL is made possible using a microfluidic cell. Upon exposure to HSA, virus-PEDOT films show a prompt increase in Zre within 5 s and a stable Zre signal within 15 min. HSA concentrations in the range from 100 nM to 5 μM are detectable. Sensor-to-sensor reproducibility of the HSA measurement is characterized by a coefficient-of-variance (COV) ranging from 2% to 8% across this entire concentration range. In addition, virus-PEDOT sensors successfully detected HSA in synthetic urine solutions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): The biosensor described here has been licensed to PhageTech, a company co-founded by Drs. Penner and Weiss. PhageTech is developing products related to the research descrived here.
The terms of this arrangement have been reviewed and approved by the University of California, Irvine in accordance with its conflict of interest politics.
Figures
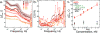
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

