Chondrogenic progenitor cells promote vascular endothelial growth factor expression through stromal-derived factor-1
- PMID: 27989872
- PMCID: PMC6367939
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2016.10.017
Chondrogenic progenitor cells promote vascular endothelial growth factor expression through stromal-derived factor-1
Abstract
Objective: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is elevated in joint fluids from patients diagnosed with osteoarthritis (OA). VEGF is known to contribute to vascular tidemark invasion and osteophyte formation, which are classic features of advanced OA. Among the factors that may drive VEGF accumulation in diseased joints, stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α) is a likely culprit, as it is enriched in synovial fluids from osteoarthritic joints and is a potent inducer of VEGF expression. Chondrogenic progenitor cells (CPCs) that overexpress SDF-1α are abundant in osteoarthritic cartilage, implicating them in elevating synovial SDF-1α levels. Here we conducted a series of experiments to determine the potential for CPCs to stimulate VEGF expression via autocrine and paracrine mechanisms.
Design: Immunohistochemistry, immunoblotting, and PCR were used to evaluate the effects of SDF-1α on VEGF expression in CPCs and chondrocytes, and the effects of CPC-conditioned medium on chondrocytes. An SDF-1α receptor antagonist and inhibitors of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) were used to probe the pathway linking SDF-1 with VEGF expression in CPCs.
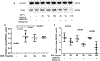
Results: SDF-1α and CPC-conditioned medium stimulated VEGF expression in chondrocytes. In both chondrocytes and CPCs, SDF-1α stimulated increased VEGF expression via C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), a cell-surface SDF-1α receptor. This response in CPCs is dependent on p38 MAPK activation, but not on ERK or c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activation.
Conclusions: By secreting SDF-1α, CPCs stimulate VEGF expression in nearby cells. The co-expression of SDF-1 and its receptor by CPCs indicates they are capable of self-sustained VEGF expression via an autocrine mechanism.
Keywords: CXCR4; Chondrogenic progenitor cells (CPCs); SDF-1α; Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF); p38 MAPK.
Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No conflicts of interest were declared.
Figures

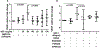

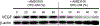
Similar articles
-
Stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha (SDF-1alpha) induces gene-expression of early growth response-1 (Egr-1) and VEGF in human arterial endothelial cells and enhances VEGF induced cell proliferation.Cell Prolif. 2003 Apr;36(2):75-86. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2184.2003.00262.x. Cell Prolif. 2003. PMID: 12680875 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium Hyaluronate-PDGF Repairs Cartilage and Subchondral Bone Microenvironment via HIF-1α-VEGF-Notch and SDF-1-CXCR4 Inhibition in Osteoarthritis.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Apr;29(7):e70515. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70515. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40159624 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms and their receptors are expressed in human osteoarthritic cartilage.Am J Pathol. 2003 Jan;162(1):171-81. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63808-4. Am J Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12507900 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically manipulated progenitor/stem cells restore function to the infarcted heart via the SDF-1α/CXCR4 signaling pathway.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2012;111:265-84. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-398459-3.00012-5. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2012. PMID: 22917235 Review.
-
[Effects of cartilage progenitor cells and microRNA-140 on repair of osteoarthritic cartilage injury].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 May 15;33(5):650-658. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201806060. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31090363 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Pathological progression of osteoarthritis: a perspective on subchondral bone.Front Med. 2024 Apr;18(2):237-257. doi: 10.1007/s11684-024-1061-y. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Front Med. 2024. PMID: 38619691 Review.
-
Isolation and Characterization of Articular Cartilage-Derived Cells Obtained by Arthroscopic Cartilage Biopsy from Non-Osteoarthritic Patients.Cells. 2025 Jun 3;14(11):830. doi: 10.3390/cells14110830. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40498006 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell transcriptomics reveals variable trajectories of CSPCs in the progression of osteoarthritis.Heliyon. 2022 Oct 18;8(11):e11148. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11148. eCollection 2022 Nov. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36339749 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) suppresses the NLRP3 inflammasome and inhibits pyroptosis in synoviocytes from osteoarthritic joints via activation of the AMPK signaling pathway.Inflammopharmacology. 2021 Jun;29(3):695-704. doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00814-x. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Inflammopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34085175 Free PMC article.
-
From regeneration to osteoarthritis in the knee joint: The role shift of cartilage-derived progenitor cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Oct 20;10:1010818. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1010818. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36340024 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Guilbert JJ. The world health report 2002 - reducing risks, promoting healthy life. Educ Health (Abingdon) 2003; 16: 230. - PubMed
-
- Ludin A, Sela JJ, Schroeder A, Samuni Y, Nitzan DW, Amir G. Injection of vascular endothelial growth factor into knee joints induces osteoarthritis in mice. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2013; 21: 491–497. - PubMed
-
- Pesesse L, Sanchez C, Delcour JP, Bellahcene A, Baudouin C, Msika P, et al. Consequences of chondrocyte hypertrophy on osteoarthritic cartilage: potential effect on angiogenesis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2013; 21: 1913–1923. - PubMed
-
- Fernandes JC, Martel-Pelletier J, Pelletier JP. The role of cytokines in osteoarthritis pathophysiology. Biorheology 2002; 39: 237–246. - PubMed
-
- Chim SM, Tickner J, Chow ST, Kuek V, Guo B, Zhang G, et al. Angiogenic factors in bone local environment. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2013; 24: 297–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

