Chondrogenic progenitor cells promote vascular endothelial growth factor expression through stromal-derived factor-1
- PMID: 27989872
- PMCID: PMC6367939
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2016.10.017
Chondrogenic progenitor cells promote vascular endothelial growth factor expression through stromal-derived factor-1
Abstract
Objective: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is elevated in joint fluids from patients diagnosed with osteoarthritis (OA). VEGF is known to contribute to vascular tidemark invasion and osteophyte formation, which are classic features of advanced OA. Among the factors that may drive VEGF accumulation in diseased joints, stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α) is a likely culprit, as it is enriched in synovial fluids from osteoarthritic joints and is a potent inducer of VEGF expression. Chondrogenic progenitor cells (CPCs) that overexpress SDF-1α are abundant in osteoarthritic cartilage, implicating them in elevating synovial SDF-1α levels. Here we conducted a series of experiments to determine the potential for CPCs to stimulate VEGF expression via autocrine and paracrine mechanisms.
Design: Immunohistochemistry, immunoblotting, and PCR were used to evaluate the effects of SDF-1α on VEGF expression in CPCs and chondrocytes, and the effects of CPC-conditioned medium on chondrocytes. An SDF-1α receptor antagonist and inhibitors of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) were used to probe the pathway linking SDF-1 with VEGF expression in CPCs.
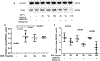
Results: SDF-1α and CPC-conditioned medium stimulated VEGF expression in chondrocytes. In both chondrocytes and CPCs, SDF-1α stimulated increased VEGF expression via C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), a cell-surface SDF-1α receptor. This response in CPCs is dependent on p38 MAPK activation, but not on ERK or c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activation.
Conclusions: By secreting SDF-1α, CPCs stimulate VEGF expression in nearby cells. The co-expression of SDF-1 and its receptor by CPCs indicates they are capable of self-sustained VEGF expression via an autocrine mechanism.
Keywords: CXCR4; Chondrogenic progenitor cells (CPCs); SDF-1α; Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF); p38 MAPK.
Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No conflicts of interest were declared.
Figures

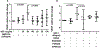

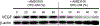
References
-
- Guilbert JJ. The world health report 2002 - reducing risks, promoting healthy life. Educ Health (Abingdon) 2003; 16: 230. - PubMed
-
- Ludin A, Sela JJ, Schroeder A, Samuni Y, Nitzan DW, Amir G. Injection of vascular endothelial growth factor into knee joints induces osteoarthritis in mice. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2013; 21: 491–497. - PubMed
-
- Pesesse L, Sanchez C, Delcour JP, Bellahcene A, Baudouin C, Msika P, et al. Consequences of chondrocyte hypertrophy on osteoarthritic cartilage: potential effect on angiogenesis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2013; 21: 1913–1923. - PubMed
-
- Fernandes JC, Martel-Pelletier J, Pelletier JP. The role of cytokines in osteoarthritis pathophysiology. Biorheology 2002; 39: 237–246. - PubMed
-
- Chim SM, Tickner J, Chow ST, Kuek V, Guo B, Zhang G, et al. Angiogenic factors in bone local environment. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2013; 24: 297–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

