Transcaval Access and Closure for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: A Prospective Investigation
- PMID: 27989885
- PMCID: PMC5291753
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.10.024
Transcaval Access and Closure for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: A Prospective Investigation
Abstract
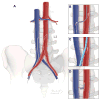
Background: Transcaval access may enable fully percutaneous transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) without the hazards and discomfort of transthoracic (transapical or transaortic) access.
Objectives: The authors performed a prospective, independently adjudicated, multicenter, single-arm trial of transcaval access for TAVR in patients who were ineligible for femoral artery access and had high or prohibitive risk of complications from transthoracic access.
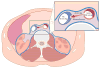
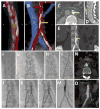
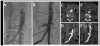
Methods: A total of 100 patients underwent attempted percutaneous transcaval access to the abdominal aorta by electrifying a caval guidewire and advancing it into a pre-positioned aortic snare. After exchanging for a rigid guidewire, conventional TAVR was performed through transcaval introducer sheaths. Transcaval access ports were closed with nitinol cardiac occluders. A core laboratory analyzed pre-discharge and 30-day abdominal computed tomograms. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons predicted risk of mortality was 9.6 ± 6.3%.
Results: Transcaval access was successful in 99 of 100 patients. Device success (access and closure with a nitinol cardiac occluder without death or emergency surgical rescue) occurred 98 of 99 patients; 1 subject had closure with a covered stent. Inpatient survival was 96%, and 30-day survival was 92%. Second Valve Academic Research Consortium (VARC-2) life-threatening bleeding and modified VARC-2 major vascular complications possibly related to transcaval access were 7% and 13%, respectively. Median length of stay was 4 days (range 2 to 6 days). There were no vascular complications after discharge.
Conclusions: Transcaval access enabled TAVR in patients who were not good candidates for transthoracic access. Bleeding and vascular complications, using permeable nitinol cardiac occluders to close the access ports, were common but acceptable in this high-risk cohort. Transcaval access should be investigated in patients who are eligible for transthoracic access. Purpose-built closure devices are in development that may simplify the procedure and reduce bleeding. (Transcaval Access for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in People With No Good Options for Aortic Access; NCT02280824).
Keywords: caval-aortic access; nontransfemoral access; structural heart disease; transcatheter aortic valve replacement; transcaval; vascular access.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

Comment in
-
The Caval-Aortic Access for Performing TAVR: Pushing the Limits of Alternative Access for Nontransfemoral Candidates.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017 Feb 7;69(5):522-525. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.11.038. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28153108 No abstract available.
References
-
- Leon MB, Smith CR, Mack M, et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve implantation for aortic stenosis in patients who cannot undergo surgery. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1597–607. - PubMed
-
- Popma JJ, Adams DH, Reardon MJ, et al. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement using a self-expanding bioprosthesis in patients with severe aortic stenosis at extreme risk for surgery. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:1972–81. - PubMed
-
- Smith CR, Leon MB, Mack MJ, et al. Transcatheter versus surgical aortic-valve replacement in high-risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:2187–98. - PubMed
-
- Adams DH, Popma JJ, Reardon MJ, et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve replacement with a self-expanding prosthesis. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1790–8. - PubMed
-
- Descoutures F, Himbert D, Maisano F, et al. Transcatheter valve-in-ring implantation after failure of surgical mitral repair. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2013;44:e8–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

