Estrogen receptor alpha promotes lupus in (NZB×NZW)F1 mice in a B cell intrinsic manner
- PMID: 27989899
- PMCID: PMC5316311
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2016.10.011
Estrogen receptor alpha promotes lupus in (NZB×NZW)F1 mice in a B cell intrinsic manner
Abstract
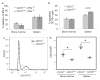
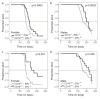
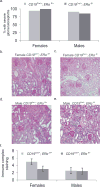
Lupus is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by the production of autoreactive antibodies against nuclear antigens. Women are disproportionately affected by lupus, and this sex bias is thought to be due, in large part, to the ability of estrogens to promote lupus pathogenesis. Previously, we have shown that global deletion of estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) significantly attenuated loss of tolerance, immune cell activation, autoantibody production, and the development of lupus nephritis. Here we show that targeted deletion of ERα specifically in B cells retards production of pathogenic autoantibodies and the development of nephritis in lupus-prone (NZB×NZW)F1 mice. Furthermore, we observed that ERα deletion in B cells was associated with decreased B cell activation in young, pre-autoimmune (NZB×NZW)F1 females. Altogether, these data suggest that ERα acts in a B cell-intrinsic manner to control B cell activation, autoantibody production, and lupus nephritis.
Keywords: B cell; Estrogen receptor alpha; Immune cell activation; Immunologic tolerance; Lupus.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Lupus nephritis: B-cell ERα signalling promotes lupus development.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017 Jan;13(1):2. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2016.167. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 27840420 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Identification of new pathogenic players in lupus: autoantibody-secreting cells are present in nephritic kidneys of (NZBxNZW)F1 mice.J Immunol. 2010 Apr 1;184(7):3937-45. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902595. Epub 2010 Feb 24. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20181885
-
Estrogen Receptor Alpha Signaling Is Responsible for the Female Sex Bias in the Loss of Tolerance and Immune Cell Activation Induced by the Lupus Susceptibility Locus Sle1b.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 10;11:582214. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.582214. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33240270 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial effects of the anti-oestrogen tamoxifen on systemic lupus erythematosus of (NZBxNZW)F1 female mice are associated with specific reduction of IgG3 autoantibodies.Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Apr;62(4):341-6. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.4.341. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003. PMID: 12634234 Free PMC article.
-
Origins of pathogenic anti-DNA idiotypes in the NZB X SWR model of lupus nephritis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;475:47-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb20855.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986. PMID: 2947530 Review.
-
Nuclease deficiencies promote end-stage lupus nephritis but not nephritogenic autoimmunity in (NZB × NZW) F1 mice.Immunol Cell Biol. 2011 Jan;89(1):90-9. doi: 10.1038/icb.2010.75. Epub 2010 Jun 15. Immunol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 20548325 Review.
Cited by
-
Sex bias in systemic lupus erythematosus: a molecular insight.Immunometabolism (Cobham). 2022 Jul 29;4(3):e00004. doi: 10.1097/IN9.0000000000000004. eCollection 2022 Jul. Immunometabolism (Cobham). 2022. PMID: 35966636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen and estrogen receptors in kidney diseases.Ren Fail. 2021 Jan 1;43(1):619-642. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2021.1901739. Ren Fail. 2021. PMID: 33784950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex hormones affect the pathogenesis and clinical characteristics of systemic lupus erythematosus.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 11;9:906475. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.906475. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36035435 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the therapeutic mechanism of Jiedu-Quyu-Ziyin Fang on systemic lupus erythematosus through the ERα-miRNA-TLR7 immune axis.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 8;10(12):e32752. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32752. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38948043 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Phenotype and Enhanced Antibody-Producing Ability of Peripheral B Cells in Mice with Cd19-Driven Cre Expression.Cells. 2022 Feb 16;11(4):700. doi: 10.3390/cells11040700. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35203346 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Azeredo da Silveira S, Kikuchi S, Fossati-Jimack L, Moll T, Saito T, Verbeek JS, Botto M, Walport MJ, Carroll M, Izui S. Complement activation selectively potentiates the pathogenicity of the IgG2b and IgG3 isotypes of a high affinity anti-erythrocyte autoantibody. J Exp Med. 2002;195:665–672. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Korganow AS, Knapp AM, Nehme-Schuster H, Soulas-Sprauel P, Poindron V, Pasquali JL, Martin T. Peripheral B cell abnormalities in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in quiescent phase: decreased memory B cells and membrane CD19 expression. J Autoimmun. 2010;34:426–434. - PubMed
-
- Gao N, Dresel J, Eckstein V, Gellert R, Storch H, Venigalla RK, Schwenger V, Max R, Blank N, Lorenz HM, Tretter T. Impaired suppressive capacity of activation-induced regulatory B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66:2849–2861. - PubMed
-
- Koide J, Takano M, Takeuchi T, Hosono O, Amano K, Homma M, Abe T. Direct demonstration of immunoregulatory T-cell defects in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Immunol. 1986;23:449–459. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

