Epobis is a Nonerythropoietic and Neuroprotective Agonist of the Erythropoietin Receptor with Anti-Inflammatory and Memory Enhancing Effects
- PMID: 27990061
- PMCID: PMC5136666
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/1346390
Epobis is a Nonerythropoietic and Neuroprotective Agonist of the Erythropoietin Receptor with Anti-Inflammatory and Memory Enhancing Effects
Abstract
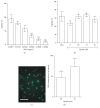
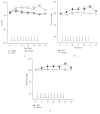
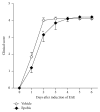
The cytokine erythropoietin (EPO) stimulates proliferation and differentiation of erythroid progenitor cells. Moreover, EPO has neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidative effects, but the use of EPO as a neuroprotective agent is hampered by its erythropoietic activity. We have recently designed the synthetic, dendrimeric peptide, Epobis, derived from the sequence of human EPO. This peptide binds the EPO receptor and promotes neuritogenesis and neuronal cell survival. Here we demonstrate that Epobis in vitro promotes neuritogenesis in primary motoneurons and has anti-inflammatory effects as demonstrated by its ability to decrease TNF release from activated AMJ2-C8 macrophages and rat primary microglia. When administered systemically Epobis is detectable in both plasma and cerebrospinal fluid, demonstrating that the peptide crosses the blood-brain barrier. Importantly, Epobis is not erythropoietic, but systemic administration of Epobis in rats delays the clinical signs of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, an animal model of multiple sclerosis, and the peptide has long-term, but not short-term, effects on working memory, detected as an improved social memory 3 days after administration. These data reveal Epobis to be a nonerythropoietic and neuroprotective EPO receptor agonist with anti-inflammatory and memory enhancing properties.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there are no financial or competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A new agonist of the erythropoietin receptor, Epobis, induces neurite outgrowth and promotes neuronal survival.J Neurochem. 2012 Jun;121(6):915-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07751.x. Epub 2012 Apr 24. J Neurochem. 2012. PMID: 22469063
-
Short erythropoietin-derived peptide enhances memory, improves long-term potentiation, and counteracts amyloid beta-induced pathology.Neurobiol Aging. 2019 Sep;81:88-101. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2019.05.003. Epub 2019 May 13. Neurobiol Aging. 2019. PMID: 31255922
-
Neuroprotective properties of a novel, non-haematopoietic agonist of the erythropoietin receptor.Brain. 2010 Aug;133(Pt 8):2281-94. doi: 10.1093/brain/awq101. Epub 2010 Apr 30. Brain. 2010. PMID: 20435631
-
Peptide Derivatives of Erythropoietin in the Treatment of Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2018;112:309-357. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2018.01.007. Epub 2018 Feb 28. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2018. PMID: 29680240 Review.
-
A Distinct Region in Erythropoietin that Induces Immuno/Inflammatory Modulation and Tissue Protection.Neurotherapeutics. 2015 Oct;12(4):850-61. doi: 10.1007/s13311-015-0379-1. Neurotherapeutics. 2015. PMID: 26271954 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Erythropoietin reduces experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis severity via neuroprotective mechanisms.J Neuroinflammation. 2017 Oct 13;14(1):202. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-0976-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2017. PMID: 29029628 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of erythropoietin on bacterial translocation in a rat model of experimental colitis.Turk J Surg. 2019 Sep 23;35(3):202-209. doi: 10.5578/turkjsurg.4272. eCollection 2019 Sep. Turk J Surg. 2019. PMID: 32550329 Free PMC article.
-
Second-generation non-hematopoietic erythropoietin-derived peptide for neuroprotection.Redox Biol. 2022 Feb;49:102223. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102223. Epub 2021 Dec 21. Redox Biol. 2022. PMID: 34953452 Free PMC article.
-
EPO activates PI3K-IKKα-CDK1 signaling pathway to promote the proliferation of Glial Cells under hypoxia environment.Genet Mol Biol. 2022 Feb 11;45(1):e20210249. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2021-0249. eCollection 2022. Genet Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35167649 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Delivery of Erythropoietin Hybridized with Magnetic Nanocarriers for the Treatment of Central Nervous System Injury: A Literature Review.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Dec 3;15:9683-9701. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S287456. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33311979 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Créange A., Lefaucheur J.-P., Balleyguier M.-O., Galactéros F. Iron depletion induced by bloodletting and followed by rhEPO administration as a therapeutic strategy in progressive multiple sclerosis: a pilot, open-label study with neurophysiological measurements. Neurophysiologie Clinique. 2013;43(5-6):303–312. doi: 10.1016/j.neucli.2013.09.004. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

