Localization of Neuropeptide Gene Expression in Larvae of an Echinoderm, the Starfish Asterias rubens
- PMID: 27990106
- PMCID: PMC5130983
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00553
Localization of Neuropeptide Gene Expression in Larvae of an Echinoderm, the Starfish Asterias rubens
Abstract
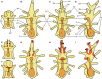
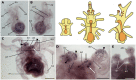
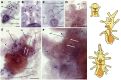
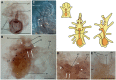
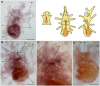
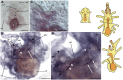
Neuropeptides are an ancient class of neuronal signaling molecules that regulate a variety of physiological and behavioral processes in animals. The life cycle of many animals includes a larval stage(s) that precedes metamorphic transition to a reproductively active adult stage but, with the exception of Drosophila melanogaster and other insects, research on neuropeptide signaling has hitherto largely focused on adult animals. However, recent advances in genome/transcriptome sequencing have facilitated investigation of neuropeptide expression/function in the larvae of protostomian (e.g., the annelid Platynereis dumerilii) and deuterostomian (e.g., the urochordate Ciona intestinalis) invertebrates. Accordingly, here we report the first multi-gene investigation of larval neuropeptide precursor expression in a species belonging to the phylum Echinodermata-the starfish Asterias rubens. Whole-mount mRNA in situ hybridization was used to visualize in bipinnaria and brachiolaria stage larvae the expression of eight neuropeptide precursors: L-type SALMFamide (S1), F-type SALMFamide (S2), vasopressin/oxytocin-type, NGFFYamide, thyrotropin-releasing hormone-type, gonadotropin-releasing hormone-type, calcitonin-type and corticotropin-releasing hormone-type. Expression of only three of the precursors (S1, S2, NGFFYamide) was observed in bipinnaria larvae but by the brachiolaria stage expression of all eight precursors was detected. An evolutionarily conserved feature of larval nervous systems is the apical organ and in starfish larvae this comprises the bilaterally symmetrical lateral ganglia, but only the S1 and S2 precursors were found to be expressed in these ganglia. A prominent feature of brachiolaria larvae is the attachment complex, comprising the brachia and adhesive disk, which mediates larval attachment to a substratum prior to metamorphosis. Interestingly, all of the neuropeptide precursors examined here are expressed in the attachment complex, with distinctive patterns of expression suggesting potential roles for neuropeptides in the attachment process. Lastly, expression of several neuropeptide precursors is associated with ciliary bands, suggesting potential roles for the neuropeptides derived from these precursors in control of larval locomotion and/or feeding. In conclusion, our findings provide novel perspectives on the evolution and development of neuropeptide signaling systems and neuroanatomical insights into neuropeptide function in echinoderm larvae.
Keywords: Echinodermata; attachment complex; bipinnaria; brachiolaria; larval nervous system; mRNA in situ hybridization; neuropeptide precursor.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

