Cysteine-Mediated Gene Expression and Characterization of the CmbR Regulon in Streptococcus pneumoniae
- PMID: 27990139
- PMCID: PMC5131005
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01929
Cysteine-Mediated Gene Expression and Characterization of the CmbR Regulon in Streptococcus pneumoniae
Abstract
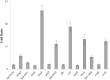
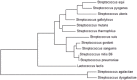
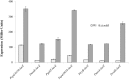
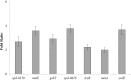
In this study, we investigated the transcriptomic response of Streptococcus pneumoniae D39 to cysteine. Transcriptome comparison of the D39 wild-type grown at a restricted concentration of cysteine (0.03 mM) to one grown at a high concentration of cysteine (50 mM) in chemically-defined medium (CDM) revealed elevated expression of various genes/operons, i.e., spd-0150, metQ, spd-0431, metEF, gshT, spd-0618, fhs, tcyB, metB-csd, metA, spd-1898, yvdE, and cysK, likely to be involved in the transport and utilization of cysteine and/or methionine. Microarray-based data were further confirmed by quantitative RT-PCR. Promoter lacZ-fusion studies and quantitative RT-PCR data showed that the transcriptional regulator CmbR acts as a transcriptional repressor of spd-0150, metEF, gshT, spd-0618, tcyB, metA, and yvdE, putatively involved in cysteine uptake and utilization. The operator site of CmbR in the promoter regions of CmbR-regulated genes is predicted and confirmed by mutating or deleting CmbR operator sites from the promoter regions of these genes.
Keywords: CmbR; Cysteine; MetA; MetE; pneumococcus.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

