Changes in IL-2 and IL-10 during Chronic Administration of Isoniazid, Nevirapine, and Paracetamol in Rats
- PMID: 27990159
- PMCID: PMC5136381
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/3094783
Changes in IL-2 and IL-10 during Chronic Administration of Isoniazid, Nevirapine, and Paracetamol in Rats
Abstract
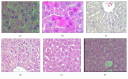
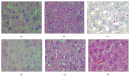
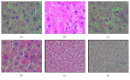
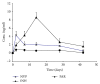
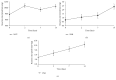
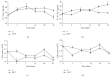
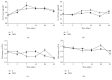
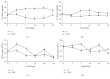
The aim of this study was to illustrate the initial subclinical drug-induced liver injury and the associated adaptive immune response by monitoring for the changes in plasma IL-2, IL-10, and some cytochrome P450 activity during chronic administration of nevirapine (NVP), isoniazid (INH), and paracetamol (PAR) in rats without clinical hepatotoxicity. Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were divided into four groups (saline (S), NVP, INH, and PAR) of 25 animals each. The drugs were administered daily for 42 days at therapeutic doses (NVP 200 mg/kg, PAR 500 mg/kg, and INH 20 mg/kg) to the respective groups by oral gavage and five rats per group were sacrificed weekly. All the three drugs induced a subclinical liver injury in the first 2-3 weeks followed by healing, indicating adaption. The liver injury was pathologically similar and was associated with immune stimulation and increased cytochrome P450 activity. NVP- and PAR-induced liver injury lasted up to 14 days while that for INH lasted for 28 days. NVP-induced liver injury was associated with increased IL-2, CD4 count, and CYP3A2 activity, followed by increased IL-10 during the healing phase. In conclusion, the initial drug-induced subclinical liver injury, its spontaneous healing, and the associated adaptive immune response have been demonstrated.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that the funding did not lead to any conflict of interests regarding the publication of this manuscript and that there are no other possible conflicts of interests in the manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Snodgrass W. R., Potter W. Z., Timbrell D. J., Mitchell J. R. Possible mechanisms of isoniazid-related hepatic injury. Clinical Research. 1975;22, article 323A
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

