The development of non-coding RNA ontology
- PMID: 27990175
- PMCID: PMC5156483
- DOI: 10.1504/IJDMB.2016.077072
The development of non-coding RNA ontology
Abstract
Identification of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) has been significantly improved over the past decade. On the other hand, semantic annotation of ncRNA data is facing critical challenges due to the lack of a comprehensive ontology to serve as common data elements and data exchange standards in the field. We developed the Non-Coding RNA Ontology (NCRO) to handle this situation. By providing a formally defined ncRNA controlled vocabulary, the NCRO aims to fill a specific and highly needed niche in semantic annotation of large amounts of ncRNA biological and clinical data.
Keywords: bio-ontologies; domain ontology; non-coding RNA; ontology development; reference ontology; semantic data annotation.
Figures
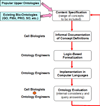
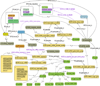
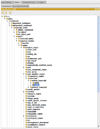
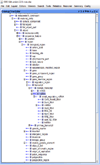
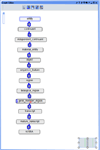
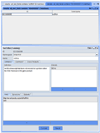
References
-
- Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 2000;25(1):25–29. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bard J. Ontologies: formalising biological knowledge for bioinformatics. Bioessays. 2003;25(5):501–506. - PubMed
-
- Blake JA. Bio-ontologies-fast and furious. Nat Biotechnol. 2004;22(6):773–774. - PubMed
-
- Blake JA, Bult CJ. Beyond the data deluge: data integration and bio-ontologies. J. Biomed Inform. 2006;39(3):314–320. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
