Molecular interrogation of hypothalamic organization reveals distinct dopamine neuronal subtypes
- PMID: 27991900
- PMCID: PMC7615022
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.4462
Molecular interrogation of hypothalamic organization reveals distinct dopamine neuronal subtypes
Abstract
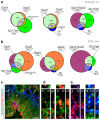
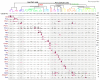
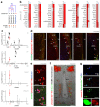
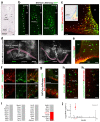
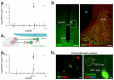
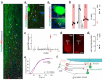
The hypothalamus contains the highest diversity of neurons in the brain. Many of these neurons can co-release neurotransmitters and neuropeptides in a use-dependent manner. Investigators have hitherto relied on candidate protein-based tools to correlate behavioral, endocrine and gender traits with hypothalamic neuron identity. Here we map neuronal identities in the hypothalamus by single-cell RNA sequencing. We distinguished 62 neuronal subtypes producing glutamatergic, dopaminergic or GABAergic markers for synaptic neurotransmission and harboring the ability to engage in task-dependent neurotransmitter switching. We identified dopamine neurons that uniquely coexpress the Onecut3 and Nmur2 genes, and placed these in the periventricular nucleus with many synaptic afferents arising from neuromedin S+ neurons of the suprachiasmatic nucleus. These neuroendocrine dopamine cells may contribute to the dopaminergic inhibition of prolactin secretion diurnally, as their neuromedin S+ inputs originate from neurons expressing Per2 and Per3 and their tyrosine hydroxylase phosphorylation is regulated in a circadian fashion. Overall, our catalog of neuronal subclasses provides new understanding of hypothalamic organization and function.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Financial Interests Statement
T.Ha. declares support from GW Pharmaceuticals on projects unrelated to the focus of this report. All other authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Du Vigneaud V. Hormones of the posterior pituitary gland: oxytocin and vasopressin. Harvey lectures. 1954;50:1–26. - PubMed
-
- Clarke IJ. Hypothalamus as an endocrine organ. Comprehensive Physiology. 2015;5:217–253. - PubMed
-
- Lantos TA, Gorcs TJ, Palkovits M. Immunohistochemical mapping of neuropeptides in the premamillary region of the hypothalamus in rats. Brain research Brain research reviews. 1995;20:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Swanson LW, Kuypers HG. The paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus: cytoarchitectonic subdivisions and organization of projections to the pituitary, dorsal vagal complex, and spinal cord as demonstrated by retrograde fluorescence double-labeling methods. The Journal of comparative neurology. 1980;194:555–570. - PubMed
-
- Dahlstrom A, Fuxe K. Evidence for Existence of Monoamine-Containing Neurons in Central Nervous System.I. Demonstration of Monoamines in Cell Bodies of Brain Stem Neurons. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964;62:1–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

