Dynamics of clonal evolution in myelodysplastic syndromes
- PMID: 27992414
- PMCID: PMC8210656
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3742
Dynamics of clonal evolution in myelodysplastic syndromes
Abstract
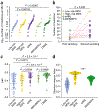
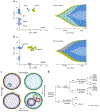
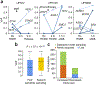
To elucidate differential roles of mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), we investigated clonal dynamics using whole-exome and/or targeted sequencing of 699 patients, of whom 122 were analyzed longitudinally. Including the results from previous reports, we assessed a total of 2,250 patients for mutational enrichment patterns. During progression, the number of mutations, their diversity and clone sizes increased, with alterations frequently present in dominant clones with or without their sweeping previous clones. Enriched in secondary acute myeloid leukemia (sAML; in comparison to high-risk MDS), FLT3, PTPN11, WT1, IDH1, NPM1, IDH2 and NRAS mutations (type 1) tended to be newly acquired, and were associated with faster sAML progression and a shorter overall survival time. Significantly enriched in high-risk MDS (in comparison to low-risk MDS), TP53, GATA2, KRAS, RUNX1, STAG2, ASXL1, ZRSR2 and TET2 mutations (type 2) had a weaker impact on sAML progression and overall survival than type-1 mutations. The distinct roles of type-1 and type-2 mutations suggest their potential utility in disease monitoring.
Figures



References
-
- Harris NL et al. World Health Organization classification of neoplastic diseases of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues: report of the Clinical Advisory Committee meeting–Airlie House, Virginia, November 1997. J. Clin. Oncol 17, 3835–3849 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Vardiman JW et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood 114, 937–951 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Malcovati L et al. Prognostic factors and life expectancy in myelodysplastic syndromes classified according to WHO criteria: a basis for clinical decision making. J. Clin. Oncol 23, 7594–7603 (2005). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

