Incidence and Risk Factors for Incident Syphilis among HIV-1-Infected Men Who Have Sex with Men in a Large Urban HIV Clinic in Tokyo, 2008-2015
- PMID: 27992604
- PMCID: PMC5161506
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168642
Incidence and Risk Factors for Incident Syphilis among HIV-1-Infected Men Who Have Sex with Men in a Large Urban HIV Clinic in Tokyo, 2008-2015
Abstract
Background: The epidemiology of incident syphilis infection among HIV-1-infected men who have sex with men (MSM) largely remains unknown.
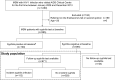
Methods: The incidence and risk factors for incident syphilis (positive TPHA and RPR> = 1:8) among HIV-1-infected MSM who visited a large HIV clinic in Tokyo for the first time between 2008 and 2013 were determined, using clinical data and stored blood samples taken every three months for screening and determination of the date of incident syphilis. Poisson regression compared the incidence of syphilis at different observation periods.
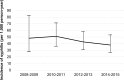
Results: Of 885 HIV-1-infected MSM with baseline data, 34% either presented with active syphilis at baseline (21%) or became infected with syphilis during follow-up (13%). After excluding 214 patients (MSM with syphilis at baseline (n = 190) and no follow-up syphilis test (n = 24)), of 671 men, 112 (17%) developed incident syphilis with an incidence of 43.7/1,000 person-years [95% CI, 36.5-52.3]. The incidence decreased slightly during observation period although the trend was not significant (2008-2009: 48.2/1,000 person-years, 2010-2011: 51.1/1,000 person-years, 2012-2013: 42.6/1,000 person-years, 2014 to 2015: 37.9/1,000 person-years, p = 0.315). Multivariable analysis identified young age (<33 years versus >40, HR 4.0, 95%CI 2.22-7.18, p<0.001), history of syphilis at baseline (HR 3.0, 95%CI 2.03-4.47, p<0.001), positive anti-amoeba antibody (HR 1.8, 95%CI 1.17-2.68, p = 0.006), and high baseline CD4 count (CD4 ≥350 /μL versus CD4 <200, HR 1.6, 95%CI 1.00-2.53, p = 0.050) as risk factors for incident syphilis. Incidence of syphilis was particularly high among young patients (age <33 years: 60.1/1,000 person-years). Interestingly, 37% of patients with incident syphilis were asymptomatic.
Conclusions: Although incidence of syphilis did not increase during the observation period, it was high among HIV-1-infected MSM, especially among young HIV-1-infected MSM and those with history of syphilis, in Tokyo. Regular screening for syphilis needs to be strictly applied to this population.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High incidence of asymptomatic syphilis in HIV-infected MSM justifies routine screening.Sex Transm Dis. 2009 Feb;36(2):84-5. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0b013e318186debb. Sex Transm Dis. 2009. PMID: 18971797
-
Incidence and risk factors for incident Hepatitis C infection among men who have sex with men with HIV-1 infection in a large Urban HIV clinic in Tokyo.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2014 Feb 1;65(2):213-7. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000000044. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2014. PMID: 24185533
-
Increasing incidence of syphilis among patients engaged in HIV care in Alberta, Canada: a retrospective clinic-based cohort study.BMC Infect Dis. 2018 Mar 13;18(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3038-4. BMC Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29534681 Free PMC article.
-
Syphilis Testing and Diagnosis Among People With Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Engaged in Care at 4 US Clinical Sites, 2014-2018.Clin Infect Dis. 2022 Aug 31;75(3):483-492. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab944. Clin Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 34788808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Musculoskeletal manifestations of syphilis in adults: secondary syphilis presenting with ankle inflammatory arthritis and bone involvement with calvarial and sternal lesions. What the rheumatologist needs to know.Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Apr;42(4):1195-1203. doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06458-8. Epub 2022 Dec 1. Clin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36454341 Review.
Cited by
-
Case-control study of risk factors for incident syphilis infection among men who have sex with men in Tokyo, Japan.Western Pac Surveill Response J. 2019 Dec 9;10(4):1-8. doi: 10.5365/wpsar.2019.10.1.003. eCollection 2019 Oct-Dec. Western Pac Surveill Response J. 2019. PMID: 32133205 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors and Incidence of Sexually Transmitted Infections in the Swiss HIV Cohort Study.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2022 Nov 16;9(12):ofac592. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofac592. eCollection 2022 Dec. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 36504700 Free PMC article.
-
High prevalence of sexually transmitted infections and risk factors among HIV-positive individuals in Yunnan, China.Eur J Med Res. 2022 Jan 13;27(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s40001-022-00635-w. Eur J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35027093 Free PMC article.
-
A cross-sectional descriptive study of clinical and serological prevalence of syphilis infection in people living with HIV and its effect on CD4+ T cells.Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2021 Jul-Dec;42(2):106-110. doi: 10.4103/ijstd.IJSTD_68_19. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2021. PMID: 34909613 Free PMC article.
-
High Prevalence of Asymptomatic STIs in MSM PWH in a Male HIV Clinic in Mexico City.J Int Assoc Provid AIDS Care. 2025 Jan-Dec;24:23259582251321039. doi: 10.1177/23259582251321039. J Int Assoc Provid AIDS Care. 2025. PMID: 39967244 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bremer V, Marcus U, Hamouda O (2012) Syphilis on the rise again in Germany—results from surveillance data for 2011. Euro Surveill 17. - PubMed
-
- AIDS Surveillance Committee. The Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare. Available: http://api-net.jfap.or.jp/status/ in Japanese. Accessed 30 May 2016.
-
- National Institute of Infectious Diseases. Infectious Diseases Weekly Report Japan. 2016 Vol 18 Issue 12. http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/id/741-disease-based/ha/syphilis/idsc/idwr-... Accessed May 30 2016.
-
- National Institute of Infectious Diseases. Infectious Diseases Weekly Report Japan. 2014 Vol 35 No. 3 http://www.nih.go.jp/niid/ja/iasr-vol35/4451-iasr-409.html. Accessed May 30 2016.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

