A KCNJ6 gene polymorphism modulates theta oscillations during reward processing
- PMID: 27993610
- PMCID: PMC5392377
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2016.12.007
A KCNJ6 gene polymorphism modulates theta oscillations during reward processing
Abstract
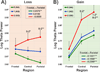
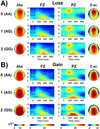
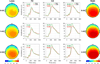
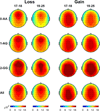
Event related oscillations (EROs) are heritable measures of neurocognitive function that have served as useful phenotype in genetic research. A recent family genome-wide association study (GWAS) by the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism (COGA) found that theta EROs during visual target detection were associated at genome-wide levels with several single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), including a synonymous SNP, rs702859, in the KCNJ6 gene that encodes GIRK2, a G-protein inward rectifying potassium channel that regulates excitability of neuronal networks. The present study examined the effect of the KCNJ6 SNP (rs702859), previously associated with theta ERO to targets in a visual oddball task, on theta EROs during reward processing in a monetary gambling task. The participants were 1601 adolescent and young adult offspring within the age-range of 17-25years (800 males and 801 females) from high-dense alcoholism families as well as control families of the COGA prospective study. Theta ERO power (3.5-7.5Hz, 200-500ms post-stimulus) was compared across genotype groups. ERO theta power at central and parietal regions increased as a function of the minor allele (A) dose in the genotype (AA>AG>GG) in both loss and gain conditions. These findings indicate that variations in the KCNJ6 SNP influence magnitude of theta oscillations at posterior loci during the evaluation of loss and gain, reflecting a genetic influence on neuronal circuits involved in reward-processing. Increased theta power as a function of minor allele dose suggests more efficient cognitive processing in those carrying the minor allele of the KCNJ6 SNPs. Future studies are needed to determine the implications of these genetic effects on posterior theta EROs as possible "protective" factors, or as indices of delays in brain maturation (i.e., lack of frontalization).
Keywords: Alcoholism; COGA; Event-related oscillations (EROs); GIRK2; KCNJ6; Monetary gambling task; Reward processing; Theta power.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Family-based genome-wide association study of frontal θ oscillations identifies potassium channel gene KCNJ6.Genes Brain Behav. 2012 Aug;11(6):712-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2012.00803.x. Epub 2012 May 31. Genes Brain Behav. 2012. PMID: 22554406 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic correlates of the development of theta event related oscillations in adolescents and young adults.Int J Psychophysiol. 2017 May;115:24-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2016.11.007. Epub 2016 Nov 12. Int J Psychophysiol. 2017. PMID: 27847216 Free PMC article.
-
Deficient Event-Related Theta Oscillations in Individuals at Risk for Alcoholism: A Study of Reward Processing and Impulsivity Features.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 18;10(11):e0142659. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142659. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26580209 Free PMC article.
-
The Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism: Overview.Genes Brain Behav. 2023 Oct;22(5):e12864. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12864. Epub 2023 Sep 22. Genes Brain Behav. 2023. PMID: 37736010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uncovering genes for cognitive (dys)function and predisposition for alcoholism spectrum disorders: a review of human brain oscillations as effective endophenotypes.Brain Res. 2008 Oct 15;1235:153-71. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.06.053. Epub 2008 Jun 24. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18634760 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Whole Genome Sequencing of Pedigrees With High Density of Substance Use and Psychiatric Disorders: A Meeting Report.Genes Brain Behav. 2025 Feb;24(1):e70017. doi: 10.1111/gbb.70017. Genes Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 39935334 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced GIRK2 channel signaling in Down syndrome: A feasible role in the development of abnormal nascent neural circuits.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 12;13:1006068. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1006068. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36171878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alcohol reverses the effects of KCNJ6 (GIRK2) noncoding variants on excitability of human glutamatergic neurons.Mol Psychiatry. 2023 Feb;28(2):746-758. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01818-x. Epub 2022 Oct 7. Mol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36207584 Free PMC article.
-
The collaborative study on the genetics of alcoholism: Genetics.Genes Brain Behav. 2023 Oct;22(5):e12856. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12856. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Genes Brain Behav. 2023. PMID: 37387240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Network preservation reveals shared and unique biological processes associated with chronic alcohol abuse in NAc and PFC.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 17;15(12):e0243857. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243857. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33332381 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander JE, Polich J, Bloom FE, Bauer LO, Kuperman S, Rohrbaugh J, Morzorati S, O’Connor SJ, Porjesz B, Begleiter H. P300 from an auditory oddball task: inter-laboratory consistency. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 1994;17:35–46. - PubMed
-
- Andreou C, Kleinert J, Steinmann S, Fuger U, Leicht G, Mulert C. Oscillatory responses to reward processing in borderline personality disorder. World J. Biol. Psychiatry. 2015:1–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

