Real-Time Monitoring of nfxB Mutant Occurrence and Dynamics in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Exposed to Subinhibitory Concentrations of Ciprofloxacin
- PMID: 27993856
- PMCID: PMC5328521
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02292-16
Real-Time Monitoring of nfxB Mutant Occurrence and Dynamics in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Exposed to Subinhibitory Concentrations of Ciprofloxacin
Abstract
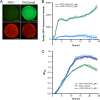
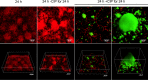
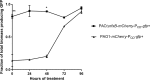
Biofilm infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa are frequently treated with ciprofloxacin (CIP); however, resistance rapidly develops. One of the primary resistance mechanisms is the overexpression of the MexCD-OprJ pump due to a mutation in nfxB, encoding the transcriptional repressor of this pump. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of subinhibitory concentrations of CIP on the occurrence of nfxB mutants in the wild-type PAO1 flow cell biofilm model. For this purpose, we constructed fluorescent reporter strains (PAO1 background) with an mCherry tag for constitutive red fluorescence and chromosomal transcriptional fusion between the P mexCD promoter and gfp leading to green fluorescence upon mutation of nfxB We observed a rapid development of nfxB mutants by live confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) imaging of the flow cell biofilm (reaching 80 to 90% of the whole population) when treated with 1/10 minimal biofilm inhibitory concentration of CIP for 24 h and 96 h. Based on the observed developmental stages, we propose that nfxB mutants emerged de novo in the biofilm during CIP treatment from filamentous cells, which might have arisen due to the stress responses induced by CIP. Identical nfxB mutations were found in fluorescent colonies from the same flow cell biofilm, especially in 24-h biofilms, suggesting selection and clonal expansion of the mutants during biofilm growth. Our findings point at the significant role of high-enough antibiotic dosages or appropriate combination therapy to avoid the emergence of resistant mutants in biofilms.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; biofilms; ciprofloxacin.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lack of the Major Multifunctional Catalase KatA in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Accelerates Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance in Ciprofloxacin-Treated Biofilms.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Sep 23;63(10):e00766-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00766-19. Print 2019 Oct. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31307984 Free PMC article.
-
Azithromycin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms: bactericidal activity and selection of nfxB mutants.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 Apr;53(4):1552-60. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01264-08. Epub 2009 Feb 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009. PMID: 19188376 Free PMC article.
-
nfxB as a novel target for analysis of mutation spectra in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 7;8(6):e66236. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066236. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23762483 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of ciprofloxacin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: new approaches to an old problem.J Med Microbiol. 2019 Jan;68(1):1-10. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000873. J Med Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30605076 Review.
-
Parallel evolution and local differentiation in quinolone resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Microbiology (Reading). 2011 Apr;157(Pt 4):937-944. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.046870-0. Epub 2011 Feb 3. Microbiology (Reading). 2011. PMID: 21292748 Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive review of the pathogenic mechanisms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: synergistic effects of virulence factors, quorum sensing, and biofilm formation.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jul 21;16:1619626. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1619626. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40761286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of antioxidant-ciprofloxacin combinations on the evolution of antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024 Dec 30;10(1):156. doi: 10.1038/s41522-024-00640-3. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024. PMID: 39738092 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting bioenergetics is key to counteracting the drug-tolerant state of biofilm-grown bacteria.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Dec 22;16(12):e1009126. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009126. eCollection 2020 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 33351859 Free PMC article.
-
Biofilm formation in Acinetobacter baumannii was inhibited by PAβN while it had no association with antibiotic resistance.Microbiologyopen. 2020 Sep;9(9):e1063. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.1063. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Microbiologyopen. 2020. PMID: 32700454 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of high-level resistance during low-level antibiotic exposure.Nat Commun. 2018 Apr 23;9(1):1599. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04059-1. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29686259 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

