Impact of coronary heart disease on cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease: a prospective longitudinal cohort study in primary care
- PMID: 27993897
- PMCID: PMC5308117
- DOI: 10.3399/bjgp16X688813
Impact of coronary heart disease on cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease: a prospective longitudinal cohort study in primary care
Abstract
Background: Arteriosclerotic disorders increase the risk of dementia. As they have common causes and risk factors, coronary heart disease (CHD) could influence the course of dementia.
Aim: To determine whether CHD increases the speed of cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease, and to discuss the potential for secondary cardiovascular prevention to modify this decline.
Design and setting: Prospective multicentre cohort study in general practices in six cities in Germany.
Method: Participants were patients with probable mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's dementia or mixed dementia (n = 118; mean age 85.6 [±3.4] years, range 80-96 years). The authors assessed the presence of CHD according to the family physicians' diagnosis. Cognitive performance was measured during home visits for up to 3 years in intervals of 6 months, using Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) and Clinical Dementia Rating Sum of Boxes (CDR-SoB). The authors also recorded whether patients died in the observation period.
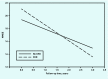
Results: At baseline, 65 patients (55%) had CHD and/or a heart condition following a myocardial infarction. The presence of CHD accelerated cognitive decline (MMSE, P<0.05) by about 66%, and reduced cognitive-functional ability (CDR-SoB, P<0.05) by about 83%, but had no impact on survival.
Conclusion: The study shows that CHD has a significant influence on cognitive decline in older patients with late-onset dementia. The dementia process might therefore be positively influenced by cardiovascular prevention, and this possible effect should be further investigated.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; cardiovascular diseases; cardiovascular risk; cognitive decline; dementia; family practice; primary health care.
© British Journal of General Practice 2017.
Figures

References
-
- Prince M, Bryce R, Albanese E, et al. The global prevalence of dementia: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Alzheimers Dement. 2013;9(1):63–75. - PubMed
-
- Verhaegen P, Borchelt M, Smith J. Relation between cardiovascular and metabolic disease and cognition in very old age: cross-sectional and longitudinal findings from the Berlin Aging Study. Health Psychol. 2003;22(6):559–569. - PubMed
-
- Casserly I, Topol EJ. Convergence of atherosclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease: inflammation, cholesterol, and misfolded proteins. Lancet. 2004;363(9415):1139–1146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
