Arterial Stiffness and Risk of Overall Heart Failure, Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction, and Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction: The Health ABC Study (Health, Aging, and Body Composition)
- PMID: 27993954
- PMCID: PMC5828168
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.08327
Arterial Stiffness and Risk of Overall Heart Failure, Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction, and Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction: The Health ABC Study (Health, Aging, and Body Composition)
Abstract
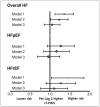
Higher arterial stiffness is associated with increased risk of atherosclerotic events. However, its contribution toward risk of heart failure (HF) and its subtypes, HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), independent of other risk factors is not well established. In this study, we included Health ABC study (Health, Aging, and Body Composition) participants without prevalent HF who had arterial stiffness measured as carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (cf-PWV) at baseline (n=2290). Adjusted Cox-proportional hazards models were constructed to determine the association between continuous and data-derived categorical measures (tertiles) of cf-PWV and incidence of HF and its subtypes (HFpEF [ejection fraction >45%] and HFrEF [ejection fraction ≤45%]). We observed 390 HF events (162 HFpEF and 145 HFrEF events) over 11.4 years of follow-up. In adjusted analysis, higher cf-PWV was associated with greater risk of HF after adjustment for age, sex, ethnicity, mean arterial pressure, and heart rate (hazard ratio [95% confidence interval] for cf-PWV tertile 3 versus tertile 1 [ref] =1.35 [1.05-1.73]). However, this association was not significant after additional adjustment for other cardiovascular risk factors (hazard ratio [95% confidence interval], 1.14 [0.88-1.47]). cf-PWV velocity was also not associated with risk of HFpEF and HFrEF after adjustment for potential confounders (most adjusted hazard ratio [95% confidence interval] for cf-PWV tertile 3 versus tertile 1 [ref]: HFpEF, 1.06 [0.72-1.56]; HFrEF, 1.28 [0.83-1.97]). In conclusion, arterial stiffness, as measured by cf-PWV, is not independently associated with risk of HF or its subtypes after adjustment for traditional cardiovascular risk factors.
Keywords: arterial stiffness; ejection fraction; heart failure; hypertension; pulse wave velocity.
© 2016 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, et al. Executive summary: heart disease and stroke statistics--2014 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2014;129:399–410. - PubMed
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, et al. Executive Summary: Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133:447–454. - PubMed
-
- Cheng RK, Cox M, Neely ML, Heidenreich PA, Bhatt DL, Eapen ZJ, Hernandez AF, Butler J, Yancy CW, Fonarow GC. Outcomes in patients with heart failure with preserved, borderline, and reduced ejection fraction in the Medicare population. Am Heart J. 2014;168:721–730. - PubMed
-
- Lam CS, Lyass A, Kraigher-Krainer E, Massaro JM, Lee DS, Ho JE, Levy D, Redfield MM, Pieske BM, Benjamin EJ, Vasan RS. Cardiac dysfunction and noncardiac dysfunction as precursors of heart failure with reduced and preserved ejection fraction in the community. Circulation. 2011;124:24–30. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

