A novel NFIA-NFκB feed-forward loop contributes to glioblastoma cell survival
- PMID: 27994064
- PMCID: PMC5473440
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/now233
A novel NFIA-NFκB feed-forward loop contributes to glioblastoma cell survival
Abstract
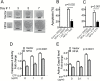
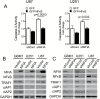
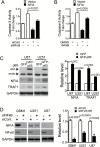
Background: The nuclear factor I-A (NFIA) transcription factor promotes glioma growth and inhibits apoptosis in glioblastoma (GBM) cells. Here we report that the NFIA pro-survival effect in GBM is mediated in part via a novel NFIA-nuclear factor-kappaB (NFκB) p65 feed-forward loop.
Methods: We examined effects of gain- and loss-of-function manipulations of NFIA and NFκB p65 on each other's transcription, cell growth, apoptosis and sensitivity to chemotherapy in patient-derived GBM cells and established GBM cell lines.
Results: NFIA enhanced apoptosis evasion by activating NFκB p65 and its downstream anti-apoptotic factors tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 1 (TRAF1) and cellular inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (cIAPs). Induction of NFκB by NFIA was required to protect cells from apoptosis, and inhibition of NFκB effectively reversed the NFIA anti-apoptotic effect. Conversely, NFIA knockdown decreased expression of NFκB and anti-apoptotic genes TRAF1 and cIAPs, and increased baseline apoptosis. NFIA positively regulated NFκB transcription and NFκB protein level. Interestingly, NFκB also activated the NFIA promoter and increased NFIA level, and knockdown of NFIA was sufficient to attenuate the NFκB pro-survival effect, suggesting a reciprocal regulation between NFIA and NFκB in governing GBM cell survival. Supporting this, NFIA and NFκB expression levels were highly correlated in human GBM and patient-derived GBM cells.
Conclusions: These data define a previously unknown NFIA-NFκB feed-forward regulation that may contribute to GBM cell survival.
Keywords: NFκB; apoptosis; chemoresistance; glioblastoma (GBM); nuclear factor I-A (NFIA).
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com
Figures



References
-
- Central Brain Tumor Registry of the United States. CBTRUS Statistical Facts Primary brain and other CNS tumor diagnosed in the United States in 2009–2013. www.cbtrus.org.
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, et al. European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumour and Radiation Oncology Groups; National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(5):459–466. - PubMed
-
- Sanai N, Berger MS. Glioma extent of resection and its impact on patient outcome. Neurosurgery. 2008;62(4):753–764; discussion 264–266. - PubMed
-
- Keles GE, Chang EF, Lamborn KR, et al. Volumetric extent of resection and residual contrast enhancement on initial surgery as predictors of outcome in adult patients with hemispheric anaplastic astrocytoma. J Neurosurg. 2006;105(1):34–40. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

