Novel Resolvin D2 Receptor Axis in Infectious Inflammation
- PMID: 27994074
- PMCID: PMC5225078
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601650
Novel Resolvin D2 Receptor Axis in Infectious Inflammation
Abstract
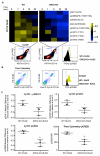
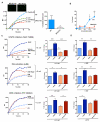
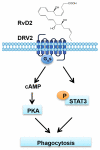
Resolution of acute inflammation is an active process governed by specialized proresolving mediators, including resolvin (Rv)D2, that activates a cell surface G protein-coupled receptor, GPR18/DRV2. In this study, we investigated RvD2-DRV2-dependent resolution mechanisms using DRV2-deficient mice (DRV2-knockout [KO]). In polymicrobial sepsis initiated by cecal ligation and puncture, RvD2 (∼2.7 nmol/mouse) significantly increased survival (>50%) of wild-type mice and reduced hypothermia and bacterial titers compared with vehicle-treated cecal ligation and puncture mice that succumbed at 48 h. Protection by RvD2 was abolished in DRV2-KO mice. Mass spectrometry-based lipid mediator metabololipidomics demonstrated that DRV2-KO infectious exudates gave higher proinflammatory leukotriene B4 and procoagulating thromboxane B2, as well as lower specialized proresolving mediators, including RvD1 and RvD3, compared with wild-type. RvD2-DRV2-initiated intracellular signals were investigated using mass cytometry (cytometry by time-of-flight), which demonstrated that RvD2 enhanced phosphorylation of CREB, ERK1/2, and STAT3 in WT but not DRV2-KO macrophages. Monitored by real-time imaging, RvD2-DRV2 interaction significantly enhanced phagocytosis of live Escherichia coli, an action dependent on protein kinase A and STAT3 in macrophages. Taken together, we identified an RvD2/DRV2 axis that activates intracellular signaling pathways that increase phagocytosis-mediated bacterial clearance, survival, and organ protection. Moreover, these results provide evidence for RvD2-DRV2 and their downstream pathways in pathophysiology of infectious inflammation.
Copyright © 2017 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of resolvin D2 receptor mediating resolution of infections and organ protection.J Exp Med. 2015 Jul 27;212(8):1203-17. doi: 10.1084/jem.20150225. Epub 2015 Jul 20. J Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26195725 Free PMC article.
-
Resolvin D2/GPR 18 axis ameliorates pressure overload-induced heart failure by inhibiting pro-inflammatory macrophage polarization.J Lipid Res. 2024 Dec;65(12):100679. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2024.100679. Epub 2024 Oct 28. J Lipid Res. 2024. PMID: 39490925 Free PMC article.
-
The resolvin D2 - GPR18 axis is expressed in human coronary atherosclerosis and transduces atheroprotection in apolipoprotein E deficient mice.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Jul;201:115075. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115075. Epub 2022 May 4. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35525326
-
Resolvin D2 and its receptor GPR18 in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases: A promising biomarker and therapeutic target.Pharmacol Res. 2023 Sep;195:106832. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106832. Epub 2023 Jun 24. Pharmacol Res. 2023. PMID: 37364787 Review.
-
Metabololipidomic profiling of functional immunoresolvent clusters and eicosanoids in mammalian tissues.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Oct 7;504(3):553-561. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.037. Epub 2018 Mar 15. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29524409 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacokinetics and Changes in Lipid Mediator Profiling after Consumption of Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid-Mediator-Enriched Marine Oil in Healthy Subjects.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 9;24(22):16143. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216143. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003333 Free PMC article.
-
Amelioration of Endotoxemia by a Synthetic Analog of Omega-3 Epoxyeicosanoids.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 24;13:825171. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.825171. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35281027 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators in Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury.Front Neurol. 2018 Jul 31;9:617. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00617. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30131754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pro-resolving lipid mediators in the resolution of neointimal hyperplasia pathogenesis in atherosclerotic diseases.Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2019 Mar;17(3):177-184. doi: 10.1080/14779072.2019.1563483. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2019. PMID: 30582389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic changes to lipid mediators support transitions among macrophage subtypes during muscle regeneration.Nat Immunol. 2019 May;20(5):626-636. doi: 10.1038/s41590-019-0356-7. Epub 2019 Apr 1. Nat Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30936495 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cotran RS. Inflammation: historical perspectives. In: Gallin JI, Snyderman R, Fearon DT, Haynes BF, Nathan C, editors. Inflammation: Basic Principles and Clinical Correlates. 3rd ed Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: 1999.
-
- Dinarello CA, Joosten LA. Inflammation in rheumatology in 2015: New tools to tackle inflammatory arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12:78–80. - PubMed
-
- Serhan CN, Clish CB, Brannon J, Colgan SP, Chiang N, Gronert K. Novel functional sets of lipid-derived mediators with antiinflammatory actions generated from omega-3 fatty acids via cyclooxygenase 2-nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs and transcellular processing. J. Exp. Med. 2000;192:1197–1204. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

