Symptom-modifying effects of oral avocado/soybean unsaponifiables in routine treatment of knee osteoarthritis in Poland. An open, prospective observational study of patients adherent to a 6-month treatment
- PMID: 27994265
- PMCID: PMC5149568
- DOI: 10.5114/reum.2016.63661
Symptom-modifying effects of oral avocado/soybean unsaponifiables in routine treatment of knee osteoarthritis in Poland. An open, prospective observational study of patients adherent to a 6-month treatment
Abstract
Objectives: Observational studies provide insights into real-life situations. Therefore, we assessed the effects of oral avocado/soybean unsaponifiable (ASU) capsules on pain relief and functional ability in patients, while they were receiving a routine treatment for knee osteoarthritis (OA).
Material and methods: An open, prospective, observational 6-month study was conducted in 99 centers in Poland in a group of 4822 patients with symptomatic knee OA receiving one 300 mg ASU capsule/day as a routine medication. The patients had no diagnoses of other rheumatic diseases and were not treated with other symptomatic slow-acting drugs for osteoarthritis (SYSADOAs). Data on OA symptoms and therapy were collected from the initiation of ASU treatment (visit 0) and during 3 consecutive control visits performed every 2 months (visits 1-3). Functional Lequesne index, severity of joint pain of one symptomatic knee (Laitinen index and VAS), use of analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), adherence to treatment and adverse events were evaluated and recorded using electronic Case Report Forms.
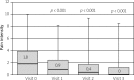
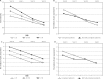
Results: Four thousand one hundred and eighty-six patients (86.8%) attended all 4 visits. In 94.2% of patients (mean age 60.7 ±11.6 years SD, 73.4% female) at least one OA risk factor was identified. There was a significant improvement in functional ability between the last and baseline visits as evidenced by the median Lequesne index decreasing from 8 to 4 points (p < 0.001). Measures of pain intensity also fell significantly (p < 0.001) throughout the study: median Laitinen score decreased from 6 to 3 points, median pain at rest VAS - from 1.8 to 0 cm and median pain during walking VAS - from 5.6 to 1.9 cm. The significant differences were also noted between consecutive visits. The proportion of patients using analgesics and NSAIDs declined from 58.8% at the baseline visit to 24.9% at the last visit 3 (p < 0.001). Defined daily dose of NSAIDs decreased significantly from 1 at the baseline visit to 0.67 at the visit 3. Severe adverse events associated with ASU treatment were not observed.
Conclusions: It was the first observational study in Poland evaluating the effects of routine knee OA treatment with oral ASU. Only a small group of patients (13.2%) treated with ASU discontinued the study. The majority of patients adherent to the ASU treatment for 6 months showed gradual alleviation of joint pain, improvement in functional ability and a significant reduction in NSAIDs intake.
Keywords: NSAIDs-sparing effect; avocado/soybean unsaponifiables; osteoarthritis treatment.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Symptomatic efficacy of avocado/soybean unsaponifiables in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee and hip: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical trial with a six-month treatment period and a two-month followup demonstrating a persistent effect.Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Jan;41(1):81-91. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199801)41:1<81::AID-ART11>3.0.CO;2-9. Arthritis Rheum. 1998. PMID: 9433873 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of avocado/soybean unsaponifiables in the treatment of symptomatic osteoarthritis of the knee and hip. A prospective, multicenter, three-month, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 1997 Dec;64(12):825-34. Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 1997. PMID: 9476272 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of avocado-soybean unsaponifiables for the treatment of hip and knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials.Int J Rheum Dis. 2019 Sep;22(9):1607-1615. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13658. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Int J Rheum Dis. 2019. PMID: 31328413
-
Symptomatic efficacy of avocado-soybean unsaponifiables (ASU) in osteoarthritis (OA) patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008 Apr;16(4):399-408. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2007.10.003. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008. PMID: 18042410 Review.
-
Structural effect of avocado/soybean unsaponifiables on joint space loss in osteoarthritis of the hip.Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Feb;47(1):50-8. doi: 10.1002/art1.10239. Arthritis Rheum. 2002. PMID: 11932878 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the novel avocado/soybean unsaponifiable Arthrocen to alter joint pain and inflammation in a rat model of osteoarthritis.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 28;13(2):e0191906. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191906. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29489828 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Effects of Arthrocen, an Avocado/Soy Unsaponifiables Agent, on Inflammation and Global Gene Expression in Human Monocytes.Int J Chem. 2017;9(4):31-39. doi: 10.5539/ijc.v9n4p31. Int J Chem. 2017. PMID: 29675116 Free PMC article.
-
Safety of Anti-osteoarthritis Medications: A Systematic Literature Review of Post-marketing Surveillance Studies.Drugs. 2025 Apr;85(4):505-555. doi: 10.1007/s40265-025-02162-4. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40095377
-
Nutraceuticals and COVID-19: A mechanistic approach toward attenuating the disease complications.J Food Biochem. 2022 Dec;46(12):e14445. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.14445. Epub 2022 Oct 14. J Food Biochem. 2022. PMID: 36239436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictive factors of adherence to an association of glucosamine sulfate, copper, and ginger extracts in patients with symptomatic osteoarthritis: a prospective open-label French noninterventional study (the PREDOA study).Patient Prefer Adherence. 2019 Jun 7;13:915-921. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S200892. eCollection 2019. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2019. PMID: 31239649 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cross M, Smith E, Hoy D, et al. The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: estimates from the the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73:1323–1330. - PubMed
-
- Bruyère O, Cooper C, Pelletier JP, et al. An algorithm recommendation for the management of knee osteoarthritis in Europe and internationally: A report from a task force of the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis (ESCEO) Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;44:253–263. - PubMed
-
- McAlindon TE, Bannuru RR, Sullivan MC, et al. OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22:363–388. - PubMed
-
- Klimiuk PA, Kuryliszyn-Moskal A. Osteoarthritis. (Aktualizacja zaleceń postępowania diagnostyczno-terapeutycznego w chorobach reumatycznych na podstawie rekomendacji EULAR/ACR) Reumatologia. 2016;(suppl. 1):111–113.
-
- Fransen M, Agaliotis M, Nairn L, et al. Glucosamine and chondroitin for knee osteoarthritis: a double-blind randomised placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluating single and combination regimes. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:851–858. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
