Cyclooxygenase-2 in tumor-associated macrophages promotes metastatic potential of breast cancer cells through Akt pathway
- PMID: 27994517
- PMCID: PMC5166494
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.15943
Cyclooxygenase-2 in tumor-associated macrophages promotes metastatic potential of breast cancer cells through Akt pathway
Abstract
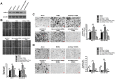
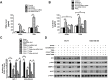
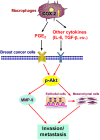
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) promote cancer development and progression by releasing various cytokines and chemokines. Previously, we have found that the number of COX-2+ TAMs was associated with lymph node metastasis in breast cancer. However, the mechanism remains enigmatic. In this study, we show that COX-2 in breast TAMs enhances the metastatic potential of breast cancer cells. COX-2 in TAMs induces MMP-9 expression and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in breast cancer cells. In addition, COX-2/PGE2 induces IL-6 release in macrophages. Furthermore, we find that the activation of Akt pathway in cancer cells is crucial for the pro-metastatic effect of COX-2+ TAMs by regulating MMP-9 and EMT. These findings indicate that TAMs facilitate breast cancer cell metastasis through COX-2-mediated intercellular communication.
Keywords: Tumor microenvironment; breast cancer; cyclooxygenase-2.; macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest in this study.
Figures



References
-
- Ostuni R, Kratochvill F, Murray PJ. et al. Macrophages and cancer: from mechanisms to therapeutic implications. Trends Immunol. 2015;36:229–39. - PubMed
-
- Sica A, Larghi P, Mancino A. et al. Macrophage polarization in tumour progression. Semin Cancer Biol. 2008;18:349–55. - PubMed
-
- Misra S, Sharma K. COX-2 signaling and cancer: new players in old arena. Curr Drug Targets. 2014;15:347–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

