Exercise Training Attenuates Right Ventricular Remodeling in Rats with Pulmonary Arterial Stenosis
- PMID: 27994552
- PMCID: PMC5136544
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00541
Exercise Training Attenuates Right Ventricular Remodeling in Rats with Pulmonary Arterial Stenosis
Abstract
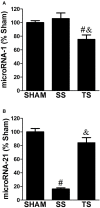
Introduction: Pulmonary arterial stenosis (PAS) is a congenital defect that causes outflow tract obstruction of the right ventricle (RV). Currently, negative issues are reported in the PAS management: not all patients may be eligible to surgeries; there is often the need for another surgery during passage to adulthood; patients with mild stenosis may have later cardiac adverse repercussions. Thus, the search for approaches to counteract the long-term PAS effects showed to be a current target. At the study herein, we evaluated the cardioprotective role of exercise training in rats submitted to PAS for 9 weeks. Methods and Results: Exercise resulted in improved physical fitness and systolic RV function. Exercise also blunted concentric cavity changes, diastolic dysfunction, and fibrosis induced by PAS. Exercise additional benefits were also reported in a pro-survival signal, in which there were increased Akt1 activity and normalized myocardial apoptosis. These findings were accompanied by microRNA-1 downregulation and microRNA-21 upregulation. Moreover, exercise was associated with a higher myocardial abundance of the sarcomeric protein α-MHC and proteins that modulate calcium handling-ryanodine receptor and Serca 2, supporting the potential role of exercise in improving myocardial performance. Conclusion: Our results represent the first demonstration that exercise can attenuate the RV remodeling in an experimental PAS. The cardioprotective effects were associated with positive modulation of RV function, survival signaling pathway, apoptosis, and proteins involved in the regulation of myocardial contractility.
Keywords: artery pulmonary stenosis; cardiac hypertrophy; cardiac remodeling; exercise training; right ventricular hypertrophy.
Figures





References
-
- Amadio E. M., Serra A. J., Guaraldo S. A., Silva J. A., Jr., Antônio E. L., Silva F., et al. (2015). The action of pre-exercise low-level laser therapy (LLLT) on the expression of IL-6 and TNF-α proteins and on the functional fitness of elderly rats subjected to aerobic training. Lasers Med. Sci. 30, 1127–1134. 10.1007/s10103-015-1713-x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ananthakrishna A., Balasubramonium V. R., Thazhath H. K., Saktheeshwaran M., Selvaraj R., Satheesh S., et al. (2014). Balloon pulmonary valvuloplasty in adults: immediate and long-term outcomes. J. Heart Valve Dis. 23, 511–515. - PubMed
-
- Baicu C. F., Li J., Zhang Y., Kasiganesan H., Cooper G., IV, Zile M. R., et al. (2012). Time course of right ventricular pressure-overload induced myocardial fibrosis: relationship to changes in fibroblast postsynthetic procollagen processing. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 303, H1128–H1134. 10.1152/ajpheart.00482.2012 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

