Ginkgo Biloba Extract EGb 761 Alleviates Hepatic Fibrosis and Sinusoidal Microcirculation Disturbance in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
- PMID: 27994702
- PMCID: PMC5154211
- DOI: 10.4021/gr2008.10.1220
Ginkgo Biloba Extract EGb 761 Alleviates Hepatic Fibrosis and Sinusoidal Microcirculation Disturbance in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
Abstract
Background: Few clinical data are available regarding the effect of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) on liver microcirculation and fibrosis. This randomized, controlled trial is to investigate the effect of Ginko biloba extract EGb 761 on liver fibrosis and hepatic microcirculation in patients with chronic hepatitis B.
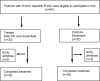
Methods: Sixty-four patients with chronic hepatitis B were randomized for intention-to-treat. Thirty-two patients were assigned to treated group receiving EGb 761 plus polyunsaturated phosphatidylcholine (Essentiale), 32 patients received Essentiale as controls. Blood samples were taken for measurement of transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGF-β1), platelet activate factor (PAF), endothelin 1 (ET-1). Twenty-six patients in treated group and 21 patients in control group underwent liver biopsies for histology before and after treatment. Ultrastructural study for sinusoidal microcirculation before and after treatment was carried out on 10 randomly selected patients in each group.
Results: In the treated group, after EGb 761 treatment, there was a significant reduction of blood TGF- β1, PAF and ET-1 (p<0.05), whereas this was not observed in the controls. After treatment in both groups, there were significant decrease of ALT, TBil and PT (p<0.05), and significant increase of ALB (p<0.05). Hepatic inflammation and fibrosis significantly alleviated in the treated group, but not in the controls. After EGb 761 treatment, electron microscopy showed red blood cell aggregates and microthrombosis disappeared or decreased in sinusoids; collagen deposits in sinusoidal lumen and Disse space reduced; sinusoidal capillarization alleviated.
Conclusions: EGb 761 can improve sinusoidal microcirculation, alleviate inflammation and inhibit fibrosis through multiple mechanisms, it is effective in the treatment of chronic liver diseases.
Keywords: Chronic Hepatitis B; EGb 761; Endothelin-1; Ginko biloba; Hepatic fibrosis; Hepatic microcirculation.
Figures


References
-
- Vellas B, Andrieu S, Ousset PJ, Ouzid M, Mathiex-Fortunet H. The GuidAge study: Methodological issues. A 5-year double-blind randomized trial of the efficacy of EGb 761(R) for prevention of Alzheimer disease in patients over 70 with a memory complaint. Neurology. 2006;67:S6–S11. - PubMed
-
- Eckert A, Keil U, Scherping I, Hauptmann S, Muller WE. Stabilization of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential and Improvement of Neuronal Energy Metabolism by Ginkgo Biloba Extract EGb 761. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1056:474–485. - PubMed
-
- Diamond BJ, Shiflett SC, Feiwel N, Matheis RJ, Noskin O, Richards JA, Schoenberger NE. Ginkgo biloba extract: mechanisms and clinical indications. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2000;81:668–678. - PubMed
-
- Varga E, Bodi A, Ferdinandy P, Droy-Lefaix MT, Blasig IE, Tosaki A. The protective effect of EGb 761 in isolated ischemic/reperfused rat hearts: a link between cardiac function and nitric oxide production. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1999;34:711–717. - PubMed
-
- Zeybek N, Gorgulu S, Yagci G, Serdar M, Simsek A, Kaymakcioglu N, Deveci S. et al. The effects of gingko biloba extract (EGb 761) on experimental acute pancreatitis. J Surg Res. 2003;115:286–293. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
