Malagasy Conostigmus (Hymenoptera: Ceraphronoidea) and the secret of scutes
- PMID: 27994960
- PMCID: PMC5157207
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.2682
Malagasy Conostigmus (Hymenoptera: Ceraphronoidea) and the secret of scutes
Abstract
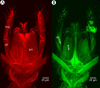
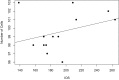
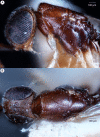
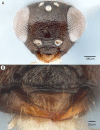
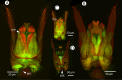
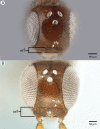
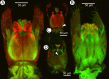
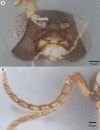
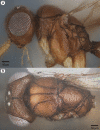
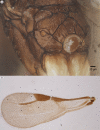
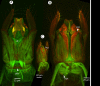
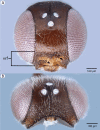
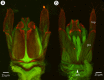
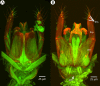
We revise the genus Conostigmus Dahlbom 1858 occurring in Madagascar, based on data from more specimens than were examined for the latest world revision of the genus. Our results yield new information about intraspecific variability and the nature of the atypical latitudinal diversity gradient (LDG) observed in Ceraphronoidea. We also investigate cellular processes that underlie body size polyphenism, by utilizing the correspondence between epidermal cells and scutes, polygonal units of leather-like microsculpture. Our results reveal that body size polyphenism in Megaspilidae is most likely related to cell number and not cell size variation, and that cell size differs between epithelial fields of the head and that of the mesosoma. Three species, Conostigmus ballescoracas Dessart, 1997, C. babaiax Dessart, 1996 and C. longulus Dessart, 1997, are redescribed. Females of C. longulus are described for the first time, as are nine new species: C. bucephalus Mikó and Trietsch sp. nov., C. clavatus Mikó and Trietsch sp. nov., C. fianarantsoaensis Mikó and Trietsch sp. nov., C. lucidus Mikó and Trietsch sp. nov., C. macrocupula, Mikó and Trietsch sp. nov., C. madagascariensis Mikó and Trietsch sp. nov., C. missyhazenae Mikó and Trietsch sp. nov., C. pseudobabaiax Mikó and Trietsch sp. nov., and C. toliaraensis Mikó and Trietsch sp. nov. A fully illustrated identification key for Malagasy Conostigmus species and a Web Ontology Language (OWL) representation of the taxonomic treatment, including specimen data, nomenclature, and phenotype descriptions, in both natural and formal languages, are provided.
Keywords: CLSM; Imaginal disks; LDG; Male genitalia; Microscopy; Morphology; Phenotypic plasticity; Taxonomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


















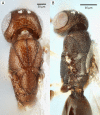

























References
-
- Al Khatib F, Fusu L, Cruaud A, Gibson G, Borowiec N, Rasplus J-Y, Ris N, Delvare G. An integrative approach to species discrimination in the Eupelmus urozonus complex (Hymenoptera, Eupelmidae), with the description of 11 new species from the Western Palaearctic. Systematic Entomology. 2014;39(4):806–862. doi: 10.1111/syen.12089. - DOI
-
- Allen RT, Ball GE. Synopsis of Mexican taxa of the Loxandrus series (Coleoptera: Carabidae: Pterostichini) Transactions of the American Entomological Society (1890-) 1979;105(4):481–575.
-
- Araj SA, Wratten SD, Lister AJ, Buckley HL. Floral nectar affects longevity of the aphid parasitoid Aphidius ervi and its hyperparasitoid Dendrocerus aphidum. New Zealand Plant Protection. 2006;59:178.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

