Impact of Gleason Pattern 5 on outcomes of patients with prostate cancer and iodine-125 prostate brachytherapy
- PMID: 27995115
- PMCID: PMC5153429
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prnil.2016.10.001
Impact of Gleason Pattern 5 on outcomes of patients with prostate cancer and iodine-125 prostate brachytherapy
Abstract
Background: The Gleason grading system is a powerful predictor of prostate cancer (PCa) prognosis. Gleason scores (GS) of 8-10 are considered as a single high-risk grade category, and Gleason Pattern 5 (GP5) predicts biochemical recurrence. We report the clinical outcomes of patients treated with 125I prostate brachytherapy for clinically localized PCa and prognosis in the presence or absence of GP5.
Methods: We enrolled 316 patients with T1c-T2N0M0 PCa and undergoing prostate brachytherapy treatment. All patients were followed up for ≥ 1 year. The primary endpoint was biochemical recurrence-free survival. Biochemical recurrence was defined by the Phoenix criteria. Survival curves were calculated by the Kaplan-Meier method, and the prognostic impact of biochemical recurrence was analyzed using a Cox proportional hazards model.
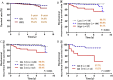
Results: The 5-year biochemical recurrence-free survival rate for all patients was 95.2%, and according to the D'Amico risk classification criteria, the rates were 98.7% for patients in low-risk, 96.9% in intermediate-risk, and 81.1% in high-risk groups (P < 0.0001). The 5-year biochemical recurrence-free survival rates for patients with GS8 or GS9-10 were 87.7% and 61.5%, respectively (P = 0.0057). Multivariate analysis found that GS and clinical T stage were independent predictors of biochemical recurrence.
Conclusions: The presence of GP5 in GS9-10 prostate cancer has a worse prognosis than GS8 prostate cancer in the absence of GP5 for patients undergoing prostate brachytherapy.
Keywords: Brachytherapy; Gleason pattern 5; Iodine-125; Prostate cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Potters L., Klein E.A., Kattan M.W., Reddy C.A., Ciezki J.P., Reuther A.M. Monotherapy for stage T1–T2 prostate cancer: radical prostatectomy, external beam radiotherapy, or permanent seed implantation. Radiother Oncol. 2004;71:29–33. - PubMed
-
- Porter C.R., Kodama K., Gibbons R.P., Correa R., Jr., Chun F.K., Perrotte P. 25-year prostate cancer control and survival outcomes: a 40-year radical prostatectomy single institution series. J Urol. 2006;176:569–574. - PubMed
-
- Sabolch A., Feng F.Y., Daignault-Newton S., Halverson S., Blas K., Phelps L. Gleason pattern 5 is the greatest risk factor for clinical failure and death from prostate cancer after dose-escalated radiation therapy and hormonal ablation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81:e351–e360. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
