oxLDL antibody inhibits MCP-1 release in monocytes/macrophages by regulating Ca2+ /K+ channel flow
- PMID: 27995732
- PMCID: PMC5387129
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13033
oxLDL antibody inhibits MCP-1 release in monocytes/macrophages by regulating Ca2+ /K+ channel flow
Abstract
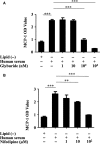
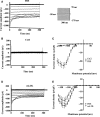
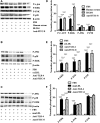
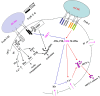
oxLDL peptide vaccine and its antibody adoptive transferring have shown a significantly preventive or therapeutic effect in atherosclerotic animal model. The molecular mechanism behind this is obscure. Here, we report that oxLDL induces MCP-1 release in monocytes/macrophages through their TLR-4 (Toll-like receptor 4) and ERK MAPK pathway and is calcium/potassium channel-dependent. Using blocking antibodies against CD36, TLR-4, SR-AI and LOX-1, only TLR-4 antibody was found to have an inhibitory effect and ERK MAPK-specific inhibitor (PD98059) was found to have a dramatic inhibitory effect compared to inhibitors of other MAPK group members (p38 and JNK MAPKs) on oxLDL-induced MCP-1 release. The release of cytokines and chemokines needs influx of extracellular calcium and imbalance of efflux of potassium. Nifedipine, a voltage-dependent calcium channel (VDCC) inhibitor, and glyburide, an ATP-regulated potassium channel (K+ATP ) inhibitor, inhibit oxLDL-induced MCP-1 release. Potassium efflux and influx counterbalance maintains the negative potential of macrophages to open calcium channels, and our results suggest that oxLDL actually induces the closing of potassium influx channel - inward rectifier channel (Kir ) and ensuing the opening of calcium channel. ERK MAPK inhibitor PD98059 inhibits oxLDL-induced Ca2+ /Kir channel alterations. The interfering of oxLDL-induced MCP-1 release by its monoclonal antibody is through its FcγRIIB (CD32). Using blocking antibodies against FcγRI (CD64), FcγRIIB (CD32) and FcγRIII (CD16), only CD32 blocking antibody was found to reverse the inhibitory effect of oxLDL antibody on oxLDL-induced MCP-1 release. Interestingly, oxLDL antibody specifically inhibits oxLDL-induced ERK MAPK activation and ensuing Ca2+ /Kir channel alterations, and MCP-1 release. Thus, we found a molecular mechanism of oxLDL antibody on inhibition of oxLDL-induced ERK MAPK pathway and consequent MCP-1 release.
Keywords: BI-204; Ca2+; FcgammarRIIB; MAPKs; MCP-1; atherosclerosis; inward rectifier K+ channel; oxLDL.
© 2016 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Quercetin modulates toll-like receptor-mediated protein kinase signaling pathways in oxLDL-challenged human PBMCs and regulates TLR-activated atherosclerotic inflammation in hypercholesterolemic rats.Mol Cell Biochem. 2016 Dec;423(1-2):53-65. doi: 10.1007/s11010-016-2824-9. Epub 2016 Sep 24. Mol Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27665434
-
Inhibition of Orai1 Store-Operated Calcium Channel Prevents Foam Cell Formation and Atherosclerosis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Apr;36(4):618-28. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.307344. Epub 2016 Feb 25. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26916730
-
Knockdown of FSTL1 inhibits oxLDL-induced inflammation responses through the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and MAPK pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Sep 30;478(4):1528-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.138. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27569284
-
Signal transduction and ion channels in guard cells.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1998 Sep 29;353(1374):1475-88. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1998.0303. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1998. PMID: 9800209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potassium and calcium channels in lymphocytes.Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:623-53. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.13.040195.003203. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7612237 Review.
Cited by
-
Recombinant Humanized IgG1 Antibody Protects against oxLDL-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Human Monocyte/Macrophage THP-1 Cells by Upregulation of MSRA via Sirt1-FOXO1 Axis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 3;23(19):11718. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911718. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233020 Free PMC article.
-
A Lipid Perspective on Regulated Pyroptosis.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Apr 25;19(8):2333-2348. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.81017. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37215994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Degree of Plasma Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Level Decrease Is Related to Clinical Outcomes for Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke.Dis Markers. 2021 Dec 14;2021:4998823. doi: 10.1155/2021/4998823. eCollection 2021. Dis Markers. 2021. PMID: 34950249 Free PMC article.
-
Top Five Stories of the Cellular Landscape and Therapies of Atherosclerosis: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives.Curr Med Sci. 2024 Feb;44(1):1-27. doi: 10.1007/s11596-023-2818-2. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Curr Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38057537 Review.
-
Mitigating atherosclerosis: Integrating vaccines with gene targets.Am Heart J Plus. 2025 Aug 6;57:100588. doi: 10.1016/j.ahjo.2025.100588. eCollection 2025 Sep. Am Heart J Plus. 2025. PMID: 40823653 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu A, Ming JY, Fiskesund R, et al Induction of dendritic cell‐mediated T‐cell activation by modified but not native low‐density lipoprotein in humans and inhibition by annexin A5: involvement of heat shock proteins. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015; 35: 197–205. - PubMed
-
- Orso E, Grandl M, Schmitz G. Oxidized LDL‐induced endolysosomal phospholipidosis and enzymatically modified LDL‐induced foam cell formation determine specific lipid species modulation in human macrophages. Chem Phys Lipids. 2011; 164: 479–87. - PubMed
-
- Miller YI, Choi SH, Fang L, et al Lipoprotein modification and macrophage uptake: role of pathologic cholesterol transport in atherogenesis. Subcell Biochem. 2010; 51: 229–51. - PubMed
-
- Koglin J, Glysing‐Jensen T, Raisanen‐Sokolowski A, et al Immune sources of transforming growth factor‐beta1 reduce transplant arteriosclerosis: insight derived from a knockout mouse model. Circ Res. 1998; 83: 652–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

