CDC-funded HIV testing, HIV positivity, and linkage to HIV medical care in non-health care settings among young men who have sex with men (YMSM) in the United States
- PMID: 27998184
- PMCID: PMC10428084
- DOI: 10.1080/09540121.2016.1271104
CDC-funded HIV testing, HIV positivity, and linkage to HIV medical care in non-health care settings among young men who have sex with men (YMSM) in the United States
Abstract
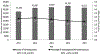
In the United States, HIV infection disproportionately affects young gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men, aged 13-24 years (collectively referred to as YMSM), specifically black YMSM. Knowledge of HIV status is the first step for timely and essential prevention and treatment services. Because YMSM are disproportionately affected by HIV, the number of CDC-funded HIV testing events, overall and newly diagnosed HIV positivity, and linkage to HIV medical care among YMSM in non-health care settings were examined from 61 health department jurisdictions. Differences by age and race/ethnicity were analyzed. Additionally, trends in number of HIV testing events and newly diagnosed HIV positivity were examined from 2011 to 2015. In 2015, 42,184 testing events were conducted among YMSM in non-health care settings; this represents only 6% of tests in non-health care settings. Overall and newly diagnosed HIV positivity was 2.8% and 2.1%, respectively, with black/African-American YMSM being disproportionately affected (5.6% for overall; 4% for newly diagnosed); 71% of YMSM were linked within 90 days. The newly diagnosed HIV positivity among YMSM decreased from 2.8% in 2011 to 2.4% in 2015, and the number of newly diagnosed YMSM also decreased. Further targeted testing efforts among YMSM are needed to identify undiagnosed YMSM, specifically black YMSM.
Keywords: HIV; diagnoses; linkage; testing; young men who have sex with men.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2012). Estimated HIV incidence in the United States, 2007–2010. HIV Surveillance Supplemental Report, 17(4). Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/statistics_hssr_vol_17_no_4.pdf
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2014). CDC-funded HIV testing: United States, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands, 2012 Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/2012_HIV_Testing_Report_01-29-15.pdf
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2015). Diagnosis of HIV infection in the United States and dependent areas, 2014. Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/library/reports/surveillance/cdc-hiv-surveill...
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2016a). CDC-funded HIV testing: United, States, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands, 2014 Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/library/reports/index.html
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
