The Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9-resistant R410S Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor Mutation: A NOVEL MECHANISM CAUSING FAMILIAL HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA
- PMID: 27998977
- PMCID: PMC5290936
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.769430
The Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9-resistant R410S Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor Mutation: A NOVEL MECHANISM CAUSING FAMILIAL HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA
Abstract
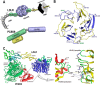
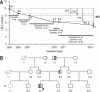
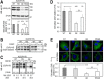
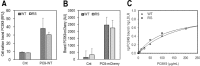
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is characterized by severely elevated low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. Herein, we identified an FH patient presenting novel compound heterozygote mutations R410S and G592E of the LDL receptor (LDLR). The patient responded modestly to maximum rosuvastatin plus ezetimibe therapy, even in combination with a PCSK9 monoclonal antibody injection. Using cell biology and molecular dynamics simulations, we aimed to define the underlying mechanism(s) by which these LDLR mutations affect LDL metabolism and lead to hypercholesterolemia. Our data showed that the LDLR-G592E is a class 2b mutant, because it mostly failed to exit the endoplasmic reticulum and was degraded. Even though LDLR-R410S and LDLR-WT were similar in levels of cell surface and total receptor and bound equally well to LDL or extracellular PCSK9, the LDLR-R410S was resistant to exogenous PCSK9-mediated degradation in endosomes/lysosomes and showed reduced LDL internalization and degradation relative to LDLR-WT. Evidence is provided for a tighter association of LDL with LDLR-R410S at acidic pH, a reduced LDL delivery to late endosomes/lysosomes, and an increased release in the medium of the bound/internalized LDL, as compared with LDLR-WT. These data suggested that LDLR-R410S recycles loaded with its LDL-cargo. Our findings demonstrate that LDLR-R410S represents an LDLR loss-of-function through a novel class 8 FH-causing mechanism, thereby rationalizing the observed phenotype.
Keywords: LDL receptor; cell biology; cholesterol metabolism; familial hypercholesterolemia; human natural mutations; loss-of-function; low density lipoprotein (LDL); lysosome; proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9); subcellular localization.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures





References
-
- LaRosa J. C., Grundy S. M., Waters D. D., Shear C., Barter P., Fruchart J. C., Gotto A. M., Greten H., Kastelein J. J., Shepherd J., Wenger N. K., and Treating to New Targets (TNT) Investigators (2005) Intensive lipid lowering with atorvastatin in patients with stable coronary disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 352, 1425–1435 - PubMed
-
- Cannon C. P., Blazing M. A., Giugliano R. P., McCagg A., White J. A., Theroux P., Darius H., Lewis B. S., Ophuis T. O., Jukema J. W., De Ferrari G. M., Ruzyllo W., De Lucca P., Im K., Bohula E. A., et al. (2015) Ezetimibe added to statin therapy after acute coronary syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 372, 2387–2397 - PubMed
-
- Brown M. S., and Goldstein J. L. (1986) A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science 232, 34–47 - PubMed
-
- Goldstein J. L., Hobbs H. H., and Brown M. S. (2001) in The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease (Valle D., Scrive C. R., Beaudet A. L., Sly W. S., Childs B., and Volgestein B., eds) pp. 2863–2913, McGraw-Hill, New York
-
- Fokkema I. F., Taschner P. E., Schaafsma G. C., Celli J., Laros J. F., and den Dunnen J. T. (2011) LOVD Version 2.0: the next generation in gene variant databases. Hum. Mutat. 32, 557–563 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

