The role of T790M mutation in EGFR-TKI re-challenge for patients with EGFR-mutant advanced lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 27999211
- PMCID: PMC5354886
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14007
The role of T790M mutation in EGFR-TKI re-challenge for patients with EGFR-mutant advanced lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
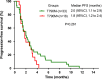
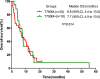
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M mutation has shown to be associated with the clinical outcomes of patients after initial EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) therapy in EGFR-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, its predictive role in EGFR-TKI re-challenge remains unknown. The present study was aimed to explore the correlation between T790M mutation and any benefits from EGFR-TKI re-challenge. We retrospectively reviewed 922 consecutive patients with EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients administered with gefitinib/erlotinib at Guangdong General Hospital. Progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), objective response rate (ORR) and disease control rate (DCR) were analyzed respectively. In total, 66 EGFR-mutant patients with stage IV adenocarcinoma were eligible, of whom 51 underwent re-biopsy upon initial progression. Among them, 18 (35.3%) harbored T790M mutation. No statistical significant differences were seen between T790M-positive and T790M-negative patients in PFS, OS, ORR or DCR. The median PFS, median OS, ORR, and DCR of the overall 66 patients were 2.0 months, 6.8 months, 6.1% and 39.4%, respectively. Good performance status (PS) was found to be independent favorable prognostic factor and long TKI-free interval to be associated with superior PFS. In conclusion, T790M mutation might not predict the clinical outcomes in first-generation EGFR-TKI re-challenge. Based on the poor efficacy from our data, re-challenge of first-generation EGFR-TKIs could not be recommended routinely, but for those with good PS and long TKI-free interval, it might be an alternative option.
Keywords: T790M mutation; TKI-free interval; adenocarcinoma; re-challenge; resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ, Wang C, Zhang S, Wang J, Zhou S, Ren S, Lu S, Zhang L, Hu C, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:735–42. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, Palmero R, Garcia-Gomez R, Pallares C, Sanchez JM, Porta R, Cobo M, Garrido P, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:239–46. - PubMed
-
- Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, Sunpaweravong P, Han B, Margono B, Ichinose Y, Nishiwaki Y, Ohe Y, Yang JJ, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:947–57. - PubMed
-
- Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S, Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, Seto T, Satouchi M, Tada H, Hirashima T, Asami K, Katakami N, Takada M, et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:121–8. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Moran T, Queralt C, Porta R, Cardenal F, Camps C, Majem M, Lopez-Vivanco G, Isla D, Provencio M, Insa A, Massuti B, Gonzalez-Larriba JL, et al. Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:958–67. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

