MicroRNAs as regulators and mediators of forkhead box transcription factors function in human cancers
- PMID: 27999212
- PMCID: PMC5355356
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14015
MicroRNAs as regulators and mediators of forkhead box transcription factors function in human cancers
Abstract
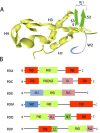
Evidence has shown that microRNAs are widely implicated as indispensable components of tumor suppressive and oncogenic pathways in human cancers. Thus, identification of microRNA targets and their relevant pathways will contribute to the development of microRNA-based therapeutics. The forkhead box transcription factors regulate numerous processes including cell cycle progression, metabolism, metastasis and angiogenesis, thereby facilitating tumor initiation and progression. A complex network of protein and non-coding RNAs mediates the expression and activity of forkhead box transcription factors. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge and concepts concerning the involvement of microRNAs and forkhead box transcription factors and describe the roles of microRNAs-forkhead box axis in various disease states including tumor initiation and progression. Additionally, we describe some of the technical challenges in the use of the microRNA-forkhead box signaling pathway in cancer treatment.
Keywords: cancer; forkhead box transcription factor; microRNA; post-transcriptional regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma by target forkhead box P4 (FOXP4).Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jan 1;8(1):337-44. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25755720 Free PMC article.
-
The upregulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5-dependent microRNA-182 and microRNA-96 promotes ovarian cancer cell proliferation by targeting forkhead box O3 upon leptin stimulation.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Mar;45(3):536-45. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.12.010. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23262295
-
MicroRNA-1269 promotes proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma via downregulation of FOXO1.BMC Cancer. 2014 Dec 3;14:909. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-909. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25472505 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Forkhead Box Class O proteins in cancer progression and metastasis.Semin Cancer Biol. 2018 Jun;50:142-151. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.07.007. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018. PMID: 28774834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on the regulation of tumor initiation and development by the forkhead box Q1 gene.J Cancer Res Ther. 2018 Jan;14(1):6-11. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_701_17. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29516951 Review.
Cited by
-
Foxp1 suppresses cortical angiogenesis and attenuates HIF-1alpha signaling to promote neural progenitor cell maintenance.EMBO Rep. 2024 May;25(5):2202-2219. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00131-8. Epub 2024 Apr 10. EMBO Rep. 2024. PMID: 38600346 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study of joint bioinformatics analysis of underlying potential of 'neurimmiR', miR-212-3P/miR-132-3P, being involved in epilepsy and its emerging role in human cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 20;8(25):40668-40682. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16541. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28380454 Free PMC article.
-
Gastric cancer cell-derived exosomal miR-541-5p induces M2 macrophage polarization through DUSP3/JAK2/STAT3 pathway.BMC Cancer. 2024 Aug 6;24(1):957. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12672-1. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39103776 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Analysis of Exosomal miR-452 and miR-4713 Downregulating NPY1R for the Prevention of Childhood Obesity.Dis Markers. 2022 Mar 30;2022:2843353. doi: 10.1155/2022/2843353. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35401881 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling the therapeutic potential of forkhead box proteins in breast cancer: An update (Review).Oncol Rep. 2024 Jul;52(1):92. doi: 10.3892/or.2024.8751. Epub 2024 Jun 7. Oncol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38847267 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Carlsson P, Mahlapuu M. Forkhead transcription factors: key players in development and metabolism. Dev Biol. 2002;250:1–23. - PubMed
-
- Zhu H. Forkhead box transcription factors in embryonic heart development and congenital heart disease. Life Sci. 2016;144:194–201. - PubMed
-
- Kaestner KH, Knochel W, Martinez DE. Unified nomenclature for the winged helix/forkhead transcription factors. Genes Dev. 2000;14:142–146. - PubMed
-
- Lam EW, Brosens JJ, Gomes AR, Koo CY. Forkhead box proteins: tuning forks for transcriptional harmony. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:482–495. - PubMed
-
- Lalmansingh AS, Karmakar S, Jin Y, Nagaich AK. Multiple modes of chromatin remodeling by Forkhead box proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1819:707–715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

