The matrix protein of rabies virus binds to RelAp43 to modulate NF-κB-dependent gene expression related to innate immunity
- PMID: 28000711
- PMCID: PMC5175135
- DOI: 10.1038/srep39420
The matrix protein of rabies virus binds to RelAp43 to modulate NF-κB-dependent gene expression related to innate immunity
Abstract
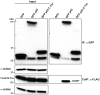
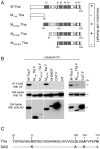
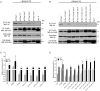
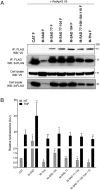
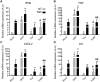
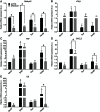
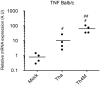
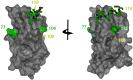
The matrix (M) protein of wild isolates of rabies virus such as Tha (M-Tha) was previously shown to be able to interact with RelAp43, a protein of the NF-κB family, and to efficiently suppress NF-κB-dependent reporter gene expression, in contrast with the vaccine strain SAD. Here, we analyze the mechanisms involved in RelAp43-M protein interaction. We demonstrate that the central part of M-Tha, and the specific C-terminal region of RelAp43 are required for this interaction. Four differences in the corresponding amino acid sequences of the M-Tha and M-SAD are shown to be crucial for RelAp43 interaction and subsequent modulation of innate immune response. Furthermore, the capacity of M-Tha to interact with RelAp43 was shown to be crucial for the control of the expression of four genes (IFN, TNF, IL8 and CXCL2) during viral infection. These findings reveal that RelAp43 is a potent regulator of transcription of genes involved in innate immune response during rabies virus infection and that the M protein of wild isolates of rabies virus is a viral immune-modulatory factor playing an important role in this RelAp43-mediated host innate immunity response in contrast to M protein of vaccine strains, which have lost this property.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of NF-κB by the p105-ABIN2-TPL2 complex and RelAp43 during rabies virus infection.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Oct 30;13(10):e1006697. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006697. eCollection 2017 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 29084252 Free PMC article.
-
RelAp43, a member of the NF-κB family involved in innate immune response against Lyssavirus infection.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(12):e1003060. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003060. Epub 2012 Dec 13. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23271966 Free PMC article.
-
Lyssavirus matrix protein cooperates with phosphoprotein to modulate the Jak-Stat pathway.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 21;9(1):12171. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48507-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31434934 Free PMC article.
-
The role of toll-like receptors in the induction of immune responses during rabies virus infection.Adv Virus Res. 2011;79:115-26. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-387040-7.00007-X. Adv Virus Res. 2011. PMID: 21601045 Review.
-
Identification and utility of innate immune system evasion mechanisms of ASFV.Virus Res. 2013 Apr;173(1):87-100. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2012.10.013. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Virus Res. 2013. PMID: 23165138 Review.
Cited by
-
Toll-like Receptors in Viral Encephalitis.Viruses. 2021 Oct 14;13(10):2065. doi: 10.3390/v13102065. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34696494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Status of antiviral therapeutics against rabies virus and related emerging lyssaviruses.Curr Opin Virol. 2019 Apr;35:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2018.12.009. Epub 2019 Feb 10. Curr Opin Virol. 2019. PMID: 30753961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure of the prefusion-locking broadly neutralizing antibody RVC20 bound to the rabies virus glycoprotein.Nat Commun. 2020 Jan 30;11(1):596. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14398-7. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32001700 Free PMC article.
-
Kinome-Wide RNA Interference Screening Identifies Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases and Phosphatidylinositol Metabolism as Key Factors for Rabies Virus Infection.mSphere. 2019 May 22;4(3):e00047-19. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00047-19. mSphere. 2019. PMID: 31118297 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte Infection during Rabies Encephalitis Depends on the Virus Strain and Infection Route as Demonstrated by Novel Quantitative 3D Analysis of Cell Tropism.Cells. 2020 Feb 11;9(2):412. doi: 10.3390/cells9020412. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32053954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thanos D. & Maniatis T. Virus induction of human IFN beta gene expression requires the assembly of an enhanceosome. Cell 83, 1091–1100, doi: 0092-8674(95)90136-1 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Verma I. M., Stevenson J. K., Schwarz E. M., Van Antwerp D. & Miyamoto S. Rel/NF-kappa B/I kappa B family: intimate tales of association and dissociation. Genes Dev 9, 2723–2735 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Saccani S., Pantano S. & Natoli G. Modulation of NF-kappaB activity by exchange of dimers. Mol Cell 11, 1563–1574, doi: S1097276503002272 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

