EhNPC1 and EhNPC2 Proteins Participate in Trafficking of Exogenous Cholesterol in Entamoeba histolytica Trophozoites: Relevance for Phagocytosis
- PMID: 28002502
- PMCID: PMC5176366
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006089
EhNPC1 and EhNPC2 Proteins Participate in Trafficking of Exogenous Cholesterol in Entamoeba histolytica Trophozoites: Relevance for Phagocytosis
Abstract
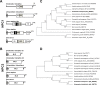
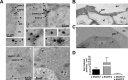
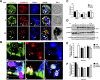
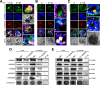
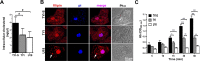
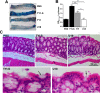
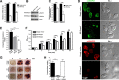
Entamoeba histolytica, the highly phagocytic protozoan causative of human amoebiasis lacks the machinery to synthesize cholesterol. Here, we investigated the presence of NPC1 and NPC2 proteins in this parasite, which are involved in cholesterol trafficking in mammals. Bioinformatics analysis revealed one Ehnpc1 and two Ehnpc2 genes. EhNPC1 appeared as a transmembrane protein and both EhNPC2 as peripheral membrane proteins. Molecular docking predicted that EhNPC1 and EhNPC2 bind cholesterol and interact with each other. Genes and proteins were identified in trophozoites. Serum pulse-chase and confocal microscopy assays unveiled that after trophozoites sensed the cholesterol source, EhNPC1 and EhNPC2 were organized around the plasma membrane in a punctuated pattern. Vesicles emerged and increased in number and size and some appeared full of cholesterol with EhNPC1 or EhNPC2 facing the extracellular space. Both proteins, but mostly EhNPC2, were found out of the cell associated with cholesterol. EhNPC1 and cholesterol formed networks from the plasma membrane to the nucleus. EhNPC2 appeared in erythrocytes that were being ingested by trophozoites, co-localizing with cholesterol of erythrocytes, whereas EhNPC1 surrounded the phagocytic cup. EhNPC1 and EhNPC2 co-localized with EhSERCA in the endoplasmic reticulum and with lysobisphosphatidic acid and EhADH (an Alix protein) in phagolysosomes. Immunoprecipitation assays confirmed the EhNPC1 and EhNPC2 association with cholesterol, EhRab7A and EhADH. Serum starved and blockage of cholesterol trafficking caused a low rate of phagocytosis and incapability of trophozoites to produce damage in the mouse colon. Ehnpc1 and Ehnpc2 knockdown provoked in trophozoites a lower intracellular cholesterol concentration and a diminished rate of phagocytosis; and Ehnpc1 silencing also produced a decrease of trophozoites movement. Trafficking of EhNPC1 and EhNPC2 during cholesterol uptake and phagocytosis as well as their association with molecules involved in endocytosis strongly suggest that these proteins play a key role in cholesterol uptake.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Lipids in Entamoeba histolytica: Host-Dependence and Virulence Factors.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Mar 10;10:75. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00075. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32211340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Sumoylation Is Crucial for Phagocytosis in Entamoeba histolytica Trophozoites.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 27;22(11):5709. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115709. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34071922 Free PMC article.
-
Entamoeba histolytica: EhADH, an Alix Protein, Participates in Several Virulence Events through Its Different Domains.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 11;25(14):7609. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147609. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062867 Free PMC article.
-
EhVps32 Is a Vacuole-Associated Protein Involved in Pinocytosis and Phagocytosis of Entamoeaba histolytica.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Jul 31;11(7):e1005079. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005079. eCollection 2015 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 26230715 Free PMC article.
-
Use and endocytosis of iron-containing proteins by Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites.Infect Genet Evol. 2009 Dec;9(6):1038-50. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2009.05.018. Epub 2009 Jun 16. Infect Genet Evol. 2009. PMID: 19539057 Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding and Treating Niemann-Pick Type C Disease: Models Matter.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 26;21(23):8979. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238979. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33256121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revisiting Drug Development Against the Neglected Tropical Disease, Amebiasis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Feb 24;10:628257. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.628257. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33718258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EhVps23: A Component of ESCRT-I That Participates in Vesicular Trafficking and Phagocytosis of Entamoeba histolytica.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Oct 29;11:770759. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.770759. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34778112 Free PMC article.
-
Lipids in Entamoeba histolytica: Host-Dependence and Virulence Factors.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Mar 10;10:75. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00075. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32211340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EhVps35, a retromer component, is a key factor in secretion, motility, and tissue invasion by Entamoeba histolytica.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Sep 27;14:1467440. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1467440. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39397861 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Das SR, Singh BN. Virulence of Strains of Entamoeba Histolytica to Rats & Guinea-Pigs, & Effect of Cholesterol on Virulence. Indian J Exp Biol. 1965;3:106–9. Epub 1965/04/01. - PubMed
-
- Mittal K, Welter BH, Temesvari LA. Entamoeba histolytica: lipid rafts are involved in adhesion of trophozoites to host extracellular matrix components. Exp Parasitol. 2008;120(2):127–34. Epub 2008/07/01. S0014-4894(08)00146-X [pii]. PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2615684. 10.1016/j.exppara.2008.06.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Welter BH, Goldston AM, Temesvari LA. Localisation to lipid rafts correlates with increased function of the Gal/GalNAc lectin in the human protozoan parasite, Entamoeba histolytica. Int J Parasitol. 2011;41(13–14):1409–19. Epub 2011/11/17. S0020-7519(11)00252-9 [pii]. PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3232469. 10.1016/j.ijpara.2011.10.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

