Cholesterol Accumulation in CD11c+ Immune Cells Is a Causal and Targetable Factor in Autoimmune Disease
- PMID: 28002731
- PMCID: PMC5181791
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.11.008
Cholesterol Accumulation in CD11c+ Immune Cells Is a Causal and Targetable Factor in Autoimmune Disease
Abstract
Liver X receptors (LXRs) are regulators of cholesterol metabolism that also modulate immune responses. Inactivation of LXR α and β in mice leads to autoimmunity; however, how the regulation of cholesterol metabolism contributes to autoimmunity is unclear. Here we found that cholesterol loading of CD11c+ cells triggered the development of autoimmunity, whereas preventing excess lipid accumulation by promoting cholesterol efflux was therapeutic. LXRβ-deficient mice crossed to the hyperlipidemic ApoE-deficient background or challenged with a high-cholesterol diet developed autoantibodies. Cholesterol accumulation in lymphoid organs promoted T cell priming and stimulated the production of the B cell growth factors Baff and April. Conversely, B cell expansion and the development of autoantibodies in ApoE/LXR-β-deficient mice was reversed by ApoA-I expression. These findings implicate cholesterol imbalance as a contributor to immune dysfunction and suggest that stimulating HDL-dependent reverse cholesterol transport could be beneficial in the setting of autoimmune disease.
Keywords: LXR; autoantibodies; autoimmune disease; reverse cholesterol transport.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
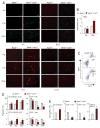

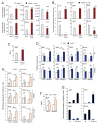
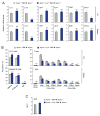
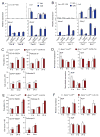

Comment in
-
Immune Cell Intolerance for Excess Cholesterol.Immunity. 2016 Dec 20;45(6):1186-1188. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.12.006. Immunity. 2016. PMID: 28002726
-
Grease fires turn up the heat in autoimmune disease.Sci Transl Med. 2017 Jan 25;9(374):eaal4997. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aal4997. Sci Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28123070
References
-
- Belalcazar LM, Merched A, Carr B, Oka K, Chen KH, Pastore L, Beaudet A, Chan L. Long-term stable expression of human apolipoprotein A-I mediated by helper-dependent adenovirus gene transfer inhibits atherosclerosis progression and remodels atherosclerotic plaques in a mouse model of familial hypercholesterolemia. Circulation. 2003;107:2726–2732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

