Short Physical Performance Battery and all-cause mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 28003033
- PMCID: PMC5178082
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-016-0763-7
Short Physical Performance Battery and all-cause mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB) is a well-established tool to assess lower extremity physical performance status. Its predictive ability for all-cause mortality has been sparsely reported, but with conflicting results in different subsets of participants. The aim of this study was to perform a meta-analysis investigating the relationship between SPPB score and all-cause mortality.
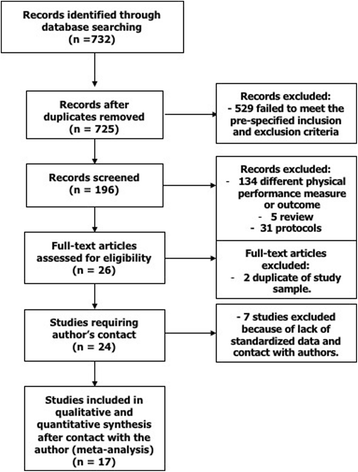
Methods: Articles were searched in MEDLINE, the Cochrane Library, Google Scholar, and BioMed Central between July and September 2015 and updated in January 2016. Inclusion criteria were observational studies; >50 participants; stratification of population according to SPPB value; data on all-cause mortality; English language publications. Twenty-four articles were selected from available evidence. Data of interest (i.e., clinical characteristics, information after stratification of the sample into four SPPB groups [0-3, 4-6, 7-9, 10-12]) were retrieved from the articles and/or obtained by the study authors. The odds ratio (OR) and/or hazard ratio (HR) was obtained for all-cause mortality according to SPPB category (with SPPB scores 10-12 considered as reference) with adjustment for age, sex, and body mass index.
Results: Standardized data were obtained for 17 studies (n = 16,534, mean age 76 ± 3 years). As compared to SPPB scores 10-12, values of 0-3 (OR 3.25, 95%CI 2.86-3.79), 4-6 (OR 2.14, 95%CI 1.92-2.39), and 7-9 (OR 1.50, 95%CI 1.32-1.71) were each associated with an increased risk of all-cause mortality. The association between poor performance on SPPB and all-cause mortality remained highly consistent independent of follow-up length, subsets of participants, geographic area, and age of the population. Random effects meta-regression showed that OR for all-cause mortality with SPPB values 7-9 was higher in the younger population, diabetics, and men.
Conclusions: An SPPB score lower than 10 is predictive of all-cause mortality. The systematic implementation of the SPPB in clinical practice settings may provide useful prognostic information about the risk of all-cause mortality. Moreover, the SPPB could be used as a surrogate endpoint of all-cause mortality in trials needing to quantify benefit and health improvements of specific treatments or rehabilitation programs. The study protocol was published on PROSPERO (CRD42015024916).
Keywords: All-cause mortality; Meta-analysis; Physical function; Short Physical Performance Battery.
Figures
References
-
- http://gamapserver.who.int/gho/interactive_charts/mbd/life_expectancy/at.... Accessed 31 July 2016.
-
- Guralnik JM, Simonsick EM, Ferrucci L, Glynn RJ, Berkman LF, Blazer DG, et al. A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function: association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission. J Gerontol. 1994;49(2):M85–94. doi: 10.1093/geronj/49.2.M85. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 DA036297/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AG048337/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG044007/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR035583/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR035584/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA004334/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG039330/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027576/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG005407/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG036921/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AG045072/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025119/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI118591/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 AI086053/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012568/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR035582/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG005394/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG044281/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials