Med Diet 4.0: the Mediterranean diet with four sustainable benefits
- PMID: 28003037
- PMCID: PMC10261651
- DOI: 10.1017/S1368980016003177
Med Diet 4.0: the Mediterranean diet with four sustainable benefits
Abstract
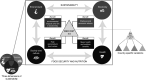
Objective: To characterize the multiple dimensions and benefits of the Mediterranean diet as a sustainable diet, in order to revitalize this intangible food heritage at the country level; and to develop a multidimensional framework - the Med Diet 4.0 - in which four sustainability benefits of the Mediterranean diet are presented in parallel: major health and nutrition benefits, low environmental impacts and richness in biodiversity, high sociocultural food values, and positive local economic returns.
Design: A narrative review was applied at the country level to highlight the multiple sustainable benefits of the Mediterranean diet into a single multidimensional framework: the Med Diet 4.0. Setting/subjects We included studies published in English in peer-reviewed journals that contained data on the characterization of sustainable diets and of the Mediterranean diet. The methodological framework approach was finalized through a series of meetings, workshops and conferences where the framework was presented, discussed and ultimately refined.
Results: The Med Diet 4.0 provides a conceptual multidimensional framework to characterize the Mediterranean diet as a sustainable diet model, by applying principles of sustainability to the Mediterranean diet.
Conclusions: By providing a broader understanding of the many sustainable benefits of the Mediterranean diet, the Med Diet 4.0 can contribute to the revitalization of the Mediterranean diet by improving its current perception not only as a healthy diet but also a sustainable lifestyle model, with country-specific and culturally appropriate variations. It also takes into account the identity and diversity of food cultures and systems, expressed within the notion of the Mediterranean diet, across the Mediterranean region and in other parts of the world. Further multidisciplinary studies are needed for the assessment of the sustainability of the Mediterranean diet to include these new dimensions.
Keywords: Food security and nutrition; Mediterranean diet; Public health nutrition; Sustainability; Sustainable diets; Sustainable food systems.
Figures
References
-
- Lang T & Barling D (2013) Nutrition and sustainability: an emerging food policy discourse. Proc Nutr Soc 72, 1–12. - PubMed
-
- Institute of Medicine (2014) Sustainable Diets: Food for Healthy People and a Healthy Planet: Workshop Summary. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. - PubMed
-
- Clonan A & Holdsworth M (2012) The challenge of eating a healthy and sustainable diet. Am J Clin Nutr 96, 459–460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources