An Expanded Transposon Mutant Library Reveals that Vibrio fischeri δ-Aminolevulinate Auxotrophs Can Colonize Euprymna scolopes
- PMID: 28003196
- PMCID: PMC5311396
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02470-16
An Expanded Transposon Mutant Library Reveals that Vibrio fischeri δ-Aminolevulinate Auxotrophs Can Colonize Euprymna scolopes
Abstract
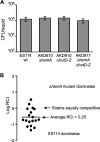
Libraries of defined mutants are valuable research tools but necessarily lack gene knockouts that are lethal under the conditions used in library construction. In this study, we augmented a Vibrio fischeri mutant library generated on a rich medium (LBS, which contains [per liter] 10 g of tryptone, 5 g of yeast extract, 20 g of NaCl, and 50 mM Tris [pH 7.5]) by selecting transposon insertion mutants on supplemented LBS and screening for those unable to grow on LBS. We isolated strains with insertions in alr, glr (murI), glmS, several heme biosynthesis genes, and ftsA, as well as a mutant disrupted 14 bp upstream of ftsQ Mutants with insertions in ftsA or upstream of ftsQ were recovered by addition of Mg2+ to LBS, but their cell morphology and motility were affected. The ftsA mutant was more strongly affected and formed cells or chains of cells that appeared to wind back on themselves helically. Growth of mutants with insertions in glmS, alr, or glr was recovered with N-acetylglucosamine (NAG), d-alanine, or d-glutamate, respectively. We hypothesized that NAG, d-alanine, or d-glutamate might be available to V. fischeri in the Euprymna scolopes light organ; however, none of these mutants colonized the host effectively. In contrast, hemA and hemL mutants, which are auxotrophic for δ-aminolevulinate (ALA), colonized at wild-type levels, although mutants later in the heme biosynthetic pathway were severely impaired or unable to colonize. Our findings parallel observations that legume hosts provide Bradyrhizobium symbionts with ALA, but they contrast with virulence phenotypes of hemA mutants in some pathogens. The results further inform our understanding of the symbiotic light organ environment.IMPORTANCE By supplementing a rich yeast-based medium, we were able to recover V. fischeri mutants with insertions in conditionally essential genes, and further characterization of these mutants provided new insights into this bacterium's symbiotic environment. Most notably, we show evidence that the squid host can provide V. fischeri with enough ALA to support its growth in the light organ, paralleling the finding that legumes provide Bradyrhizobium ALA in symbiotic nodules. Taken together, our results show how a simple method of augmenting already rich media can expand the reach and utility of defined mutant libraries.
Keywords: Aliivibrio; Photobacterium; aminolevulinic acid; hemin; photobacteria; symbiosis.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



References
-
- Jacobs MA, Alwood A, Thaipisuttikul I, Spencer D, Haugen E, Ernst S, Will O, Kaul R, Raymond C, Levy R, Chun-Rong L, Guenthner D, Bovee D, Olson MV, Manoil C. 2003. Comprehensive transposon mutant library of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:14339–14344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2036282100. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

