Differentiating lower motor neuron syndromes
- PMID: 28003344
- PMCID: PMC5529975
- DOI: 10.1136/jnnp-2016-313526
Differentiating lower motor neuron syndromes
Abstract
Lower motor neuron (LMN) syndromes typically present with muscle wasting and weakness and may arise from pathology affecting the distal motor nerve up to the level of the anterior horn cell. A variety of hereditary causes are recognised, including spinal muscular atrophy, distal hereditary motor neuropathy and LMN variants of familial motor neuron disease. Recent genetic advances have resulted in the identification of a variety of disease-causing mutations. Immune-mediated disorders, including multifocal motor neuropathy and variants of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, account for a proportion of LMN presentations and are important to recognise, as effective treatments are available. The present review will outline the spectrum of LMN syndromes that may develop in adulthood and provide a framework for the clinician assessing a patient presenting with predominantly LMN features.
Keywords: GENETICS; MOTOR NEURON DISEASE; NEUROIMMUNOLOGY; NEUROPATHY; NEUROPHYSIOLOGY.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
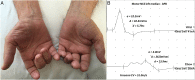
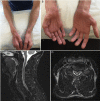
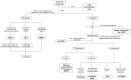
Figures


References
-
- Prior TW and Russman BS. GeneReviews [internet]: Spinal Muscular Atrophy. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1352/ (accessed Aug 2016).
-
- Wirth B, Herz M, Wetter A, et al. Quantitative analysis of survival motor neuron copies: identification of subtle SMN1 mutations in patients with spinal muscular atrophy, genotype-phenotype correlation, and implications for genetic counseling. Am J Hum Genet 1999;64:1340–56. 10.1086/302369 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
