Phosphorylation of Rap1 by cAMP-dependent Protein Kinase (PKA) Creates a Binding Site for KSR to Sustain ERK Activation by cAMP
- PMID: 28003362
- PMCID: PMC5270487
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.768986
Phosphorylation of Rap1 by cAMP-dependent Protein Kinase (PKA) Creates a Binding Site for KSR to Sustain ERK Activation by cAMP
Abstract
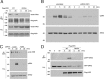
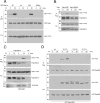
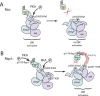
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is an important mediator of hormonal stimulation of cell growth and differentiation through its activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) cascade. Two small G proteins, Ras and Rap1 have been proposed to mediate this activation. Using HEK293 cells as a model system, we have recently shown that both Ras and Rap1 are required for cAMP signaling to ERKs. However, cAMP-dependent Ras signaling to ERKs is transient and rapidly terminated by PKA phosphorylation of the Raf isoforms C-Raf and B-Raf. In contrast, cAMP-dependent Rap1 signaling to ERKs and Rap1 is potentiated by PKA. We show that this is due to sustained binding of B-Raf to Rap1. One of the targets of PKA is Rap1 itself, directly phosphorylating Rap1a on serine 180 and Rap1b on serine 179. We show that these phosphorylations create potential binding sites for the adaptor protein 14-3-3 that links Rap1 to the scaffold protein KSR. These results suggest that Rap1 activation of ERKs requires PKA phosphorylation and KSR binding. Because KSR and B-Raf exist as heterodimers within the cell, this binding also brings B-Raf to Rap1, allowing Rap1 to couple to ERKs through B-Raf binding to Rap1 independently of its Ras-binding domain.
Keywords: 14-3-3 protein; Raf kinase; Ras-related protein 1 (Rap1); extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK); protein kinase A (PKA).
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Fujita T., Meguro T., Fukuyama R., Nakamuta H., and Koida M. (2002) New signaling pathway for parathyroid hormone and cyclic AMP action on extracellular-regulated kinase and cell proliferation in bone cells: checkpoint of modulation by cyclic AMP. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 22191–22200 - PubMed
-
- Gomez E., Pritchard C., and Herbert T. P. (2002) cAMP-dependent protein kinase and Ca2+ influx through L-type voltage-gated calcium channels mediate Raf-independent activation of extracellular regulated kinase in response to glucagon-like peptide-1 in pancreatic beta-cells. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 48146–48151 - PubMed
-
- Ehses J. A., Pelech S. L., Pederson R. A., and McIntosh C. H. (2002) Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide activates the Raf-Mek1/2-ERK1/2 module via a cyclic AMP/cAMP-dependent protein kinase/Rap1-mediated pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 37088–37097 - PubMed
-
- Morozov A., Muzzio I. A., Bourtchouladze R., Van-Strien N., Lapidus K., Yin D., Winder D. G., Adams J. P., Sweatt J. D., and Kandel E. R. (2003) Rap1 couples cAMP signaling to a distinct pool of p42/44MAPK regulating excitability, synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory. Neuron 39, 309–325 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

