Expanding the spectrum of congenital myopathy linked to recessive mutations in SCN4A
- PMID: 28003497
- PMCID: PMC5272967
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003535
Expanding the spectrum of congenital myopathy linked to recessive mutations in SCN4A
Figures
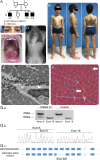
References
-
- Plassart E, Reboul J, Rime CS, et al. . Mutations in the muscle sodium channel gene (SCN4A) in 13 French families with hyperkalemic periodic paralysis and paramyotonia congenita: phenotype to genotype correlations and demonstration of the predominance of two mutations. Eur J Hum Genet 1994;2:110–124. - PubMed
-
- Ptácek LJ, Tawil R, Griggs RC, et al. . Sodium channel mutations in acetazolamide-responsive myotonia congenita, paramyotonia congenita, and hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Neurology 1994;44:1500–1503. - PubMed
-
- Sternberg D, Maisonobe T, Jurkat-Rott K, et al. . Hypokalaemic periodic paralysis type 2 caused by mutations at codon 672 in the muscle sodium channel gene SCN4A. Brain 2001;124:1091–1099. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
