Associations between dopamine D2 receptor gene polymorphisms and schizophrenia risk: a PRISMA compliant meta-analysis
- PMID: 28003749
- PMCID: PMC5158172
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S118614
Associations between dopamine D2 receptor gene polymorphisms and schizophrenia risk: a PRISMA compliant meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To determine the relationships between dopamine D2 receptor gene polymorphisms and the risk of schizophrenia using meta-analysis.
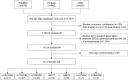
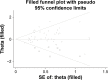
Method: The PubMed, Embase, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure databases were searched to identify relevant literature published up to February 2016. The allele contrast model was used. Stata software was used for statistical analysis, with odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) calculated to evaluate the associations between dopamine D2 receptor gene polymorphisms and the risk of schizophrenia. Meta-regression and publication bias, trim-and-fill, subgroup, sensitivity, cumulative, and fail-safe number analyses were also performed.
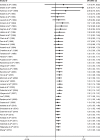
Results: This meta-analysis included 81 studies. The rs1801028 and rs1799732 were associated with schizophrenia risk among Asians (P=0.04, OR =1.25, 95% CI =1.01-1.55; P<0.01, OR =0.76, 95% CI =0.63-0.92, respectively), while the rs6277 was associated with schizophrenia risk in Caucasians (P<0.01, OR=0.72, 95% CI =0.66-0.79). The rs1800497 was also associated with schizophrenia risk in population-based controls (P<0.01, OR =0.84, 95% CI =0.72-0.97). The rs6275, rs1079597, and rs1800498 were not associated with schizophrenia risk. In addition, meta-regression indicated that the controls may be sources of heterogeneity for the rs1801028 single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), while ethnicity may be sources of heterogeneity for the rs6277 SNP. Publication bias was significant for the rs1801028 SNP, and this result changed after the publication bias was adjusted using the trim-and-fill method.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis demonstrated that the rs1801028 may be a risk factor for susceptibility to schizophrenia among Asians, while the rs1799732 may be a protective factor for that population. Large-sample studies are necessary to verify the results of this meta-analysis.
Keywords: dopamine D2 receptor; polymorphisms; schizophrenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Association between DRD2 (rs1799732 and rs1801028) and ANKK1 (rs1800497) polymorphisms and schizophrenia: a meta-analysis.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2015 Jan;168B(1):1-13. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32281. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2015. PMID: 25504812 Review.
-
Association between dopamine receptor gene polymorphisms and effects of risperidone treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019 Jan;124(1):94-104. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13111. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30103286
-
Associations of NQO1 C609T and NQO1 C465T polymorphisms with acute leukemia risk: a PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2017 Mar 23;10:1793-1801. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S132503. eCollection 2017. Onco Targets Ther. 2017. PMID: 28367062 Free PMC article.
-
Association between ANKK1 (rs1800497) polymorphism of DRD2 gene and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analysis.Neurosci Lett. 2015 Mar 17;590:101-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.01.076. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Neurosci Lett. 2015. PMID: 25641135
-
Investigating the association between common DRD2/ANKK1 genetic polymorphisms and schizophrenia: a meta-analysis.J Genet. 2021;100:59. J Genet. 2021. PMID: 34470923
Cited by
-
Influence of COMT (rs4680) and DRD2 (rs1076560, rs1800497) Gene Polymorphisms on Safety and Efficacy of Methylphenidate Treatment in Children with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Apr 8;19(8):4479. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19084479. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35457347 Free PMC article.
-
Association between DRD2 and ANKK1 polymorphisms with the deficit syndrome in schizophrenia.Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2020 Jun 17;19:39. doi: 10.1186/s12991-020-00289-0. eCollection 2020. Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32565876 Free PMC article.
-
No association between polymorphisms in the promoter region of dopamine receptor D2 gene and schizophrenia in the northern Chinese Han population: A case-control study.Brain Behav. 2019 Feb;9(2):e01193. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1193. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Brain Behav. 2019. PMID: 30657260 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine Receptor D2 Gene (DRD2) Polymorphisms, Job Stress, and Their Interaction on Sleep Dysfunction.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Nov 5;17(21):8174. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17218174. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33167416 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive exploration of the genetic contribution of the dopaminergic and serotonergic pathways to psychiatric disorders.Transl Psychiatry. 2022 Jan 10;12(1):11. doi: 10.1038/s41398-021-01771-3. Transl Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35013130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Betcheva ET, Mushiroda T, Takahashi A, et al. Case-control association study of 59 candidate genes reveals the DRD2 SNP rs6277 (C957T) as the only susceptibility factor for schizophrenia in the Bulgarian population. J Hum Genet. 2009;54(2):98–107. - PubMed
-
- Kukreti R, Tripathi S, Bhatnagar P, et al. Association of DRD2 gene variant with schizophrenia. Neurosci Lett. 2006;392(1–2):68–71. - PubMed
-
- Ohara K, Nakamura Y, Xie DW, et al. Polymorphisms of dopamine D2-like (D2, D3, and D4) receptors in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 1996;40(12):1209–1217. - PubMed
-
- Srivastava V, Deshpande SN, Thelma BK. Dopaminergic pathway gene polymorphisms and genetic susceptibility to schizophrenia among north Indians. Neuropsychobiology. 2010;61(2):64–70. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

