A pilot study employing hepatic intra-arterial irinotecan injection of drug-eluting beads as salvage therapy in liver metastatic colorectal cancer patients without extrahepatic involvement: the first southern Italy experience
- PMID: 28003766
- PMCID: PMC5161393
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S112670
A pilot study employing hepatic intra-arterial irinotecan injection of drug-eluting beads as salvage therapy in liver metastatic colorectal cancer patients without extrahepatic involvement: the first southern Italy experience
Abstract
Background: The main aim of this prospective study was to evaluate the efficacy of drug-eluting beads with irinotecan (DEBIRI) for liver metastases from colorectal cancer. Secondary aims were to evaluate survival and toxicity.
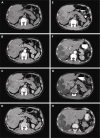
Methods: Twenty-five patients with metastases in <50% of the liver and without extrahepatic involvement were enrolled. Treatment response assessment was performed by multidetector contrast enhancement computed tomography (MDCT) with evaluation of the enhancement pattern of the target lesion and tumor response rates according to modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (mRECIST, Version 1.1). All adverse events were recorded by the Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, Version 3.0. Associations of tumor response and variables were calculated using the chi-squared test. Overall survival (OS) was calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method. Comparisons were made using the log-rank test.
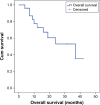
Results: According to mRECIST, complete response (CR) was observed in 21.8% of patients, partial response (PR) in 13%, stable disease (SD) in 52.2% and progressive disease (PD) in 13% of patients. Response rate (RR = CR + PR) was 34.8%. No associations between treatment response and variables such as Dukes' classification, grading and Kras status were found (P>0.05). The median OS was 37 months (95% CI: 13.881 to 60.119). Cox regression model showed that neither site, Dukes' classification, grading, Kras status nor number of chemotherapy treatments pre-DEBIRI influenced the OS. The log-rank test showed no statistically significant difference in OS among patients who underwent 1, 2 or 3 DEBIRI treatments (χ2=2.831, P=0.09). In our study, the main toxicities included postembolization syndrome (PES), hypertransaminasemia and fever.
Conclusion: The favorable tumor response and the favorable toxicity profile make DEBIRI treatment a potential third-line therapy. Although further larger studies are needed to confirm these data, we can state that DEBIRI is an attractive emerging treatment in these patients.
Keywords: DEBIRI; colorectal cancer; liver metastases; transarterial chemoembolization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Updates of colorectal cancer liver metastases therapy: review on DEBIRI.Hepat Oncol. 2020 Jan 21;7(1):HEP16. doi: 10.2217/hep-2019-0010. Hepat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32273974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transarterial chemoembolization using DEBIRI for treatment of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer.Anticancer Res. 2013 May;33(5):2077-83. Anticancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23645758
-
Efficacy and Toxicity of Hepatic Intra-Arterial Drug-Eluting (Irinotecan) Bead (DEBIRI) Therapy in Irinotecan-Refractory Unresectable Colorectal Liver Metastases.World J Surg. 2016 May;40(5):1178-90. doi: 10.1007/s00268-015-3386-9. World J Surg. 2016. PMID: 26711640
-
Hepatic intra-arterial injection of drug-eluting bead, irinotecan (DEBIRI) in unresectable colorectal liver metastases refractory to systemic chemotherapy: results of multi-institutional study.Ann Surg Oncol. 2011 Jan;18(1):192-8. doi: 10.1245/s10434-010-1288-5. Epub 2010 Aug 26. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011. PMID: 20740319
-
Drug-Eluting Bead, Irinotecan (DEBIRI) Therapy for Refractory Colorectal Liver Metastasis: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Dec 6;15(12):e50072. doi: 10.7759/cureus.50072. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38186525 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Safety, Feasibility and Technical Considerations from a Prospective, Observational Study-CIREL: Irinotecan-TACE for CRLM in 152 Patients.J Clin Med. 2022 Oct 19;11(20):6178. doi: 10.3390/jcm11206178. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36294499 Free PMC article.
-
Updates of colorectal cancer liver metastases therapy: review on DEBIRI.Hepat Oncol. 2020 Jan 21;7(1):HEP16. doi: 10.2217/hep-2019-0010. Hepat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32273974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bevacizumab Plus FOLFOX-4 Combined With Deep Electro-Hyperthermia as First-line Therapy in Metastatic Colon Cancer: A Pilot Study.Front Oncol. 2020 Nov 3;10:590707. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.590707. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33224885 Free PMC article.
-
Loco-Regional and Systemic Chemotherapies for Hepato-Pancreatic Tumors: Integrated Treatments.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 24;12(10):2737. doi: 10.3390/cancers12102737. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32987630 Free PMC article.
-
Oxaliplatin-Based Intra-arterial Chemotherapy in Colo-Rectal Cancer Liver Metastases: A Review from Pharmacology to Clinical Application.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jan 24;11(2):141. doi: 10.3390/cancers11020141. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30682873 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55(2):74–108. - PubMed
-
- Scheele J, Stangl R, Altendorf-Hofmann A, Gall FP. Indicators of prognosis after hepatic resection for colorectal secondaries. Surgery. 1991;110(1):13–29. - PubMed
-
- Kemeny NE, Kemeny MM, Lawrence TS. Liver Metastases. 3th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Clinical Oncology; 2004. pp. 1141–1178.
-
- Martin RCG, Joshi J, Robbins K, et al. Hepatic intra-arterial injection of drug-eluting bead, irinotecan (DEBIRI) in unresectable colorectal liver metastases refractory to systemic chemotherapy: results of multi-institutional study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18(1):192–198. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

